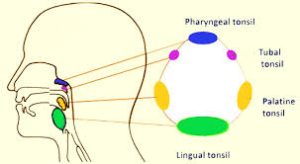
Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring is a ringed arrangement of lymphoid organs in the pharynx.
It surrounds the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate.
The ring consists of:
pharyngeal tonsil (or adenoid), located on the roof of the nasopharynx, under the sphenoid bone.
tubal tonsils on each side, where each auditory tube opens into the nasopharynx
palatine tonsils located in the oropharynx
lingual tonsils, a collection of lymphatic tissue located on the back part of the tongue
There is mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) present between these tonsils (intertonsillar) around the ring, and throughout the naso- and oropharynx.
Waldeyer’s ring circumscribes the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate.
The Waldeyer’s ring prevents the invasion of microorganisms from going into the air and food passages and this helps in the defense mechanism of the respiratory and alimentary systems.
The palatine tonsils when inflamed in children, can obstruct respiration. (Tonsillitis).
