 The hypopharynx or laryngopharynx forms the most inferior portion of the pharynx, being the continuation of the oropharynx superiorly and both the larynx and esophagus inferiorly.
The hypopharynx or laryngopharynx forms the most inferior portion of the pharynx, being the continuation of the oropharynx superiorly and both the larynx and esophagus inferiorly.
As part of the pharynx, the hypopharynx is located behind the entire length of the larynx.
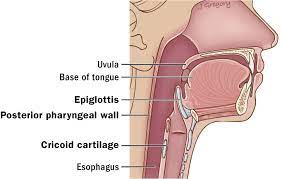
The hypopharynx extends from the plane of the epiglottis to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage.
Moreover, the pharynx is further classified into three regions: (1) the piriform sinuses, (2) the posterior pharyngeal wall, and (3) the post-cricoid area.
It also forms part of the upper respiratory tract and the gastrointestinal tract.
The hypopharynx begins as the continuation of the oropharynx at the pharyngoepiglottic fold, at the level of the hyoid bone, superiorly, and extends inferiorly to the level of the inferior aspect of the cricoid cartilage, where it continues as the cervical esophagus.
The hypopharynx is a mucosa-lined, muscular tube with its posterolateral walls formed by the inferior constrictor muscle and anterior wall by laryngeal cartilages.
The hypopharynx forms part of the pharyngeal mucosal space.
The superior boundary of the laryngopharynx is at the level of the hyoid bone located between the 4th and 6th cervical vertebrae.
Like the oropharynx above it, the laryngopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium.
It is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus.
The laryngopharynx ( hypopharynx) includes three major sites: the pyriform sinus, postcricoid area, and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
The hypopharynx boundaries:
anteriorly: post-cricoid mucosa, posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
posteriorly: mucosal wall, middle and inferior constrictor muscles
superiorly: hyoid bone, glossoepiglottic and pharyngoepiglottic folds
inferiorly: cricoid cartilage, cricopharyngeus muscle
The vascular supply to the laryngopharynx includes the superior thyroid artery, the lingual artery and the ascending pharyngeal artery.
The primary neural supply is from both the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves.
The vagus nerve provides an auricular branch which also supplies the external auditory canal, thus laryngopharyngeal cancer can result in referred ear pain.
This nerve is also responsible for the ear-cough reflex in which stimulation of the ear canal results in a person coughing.
Three subsites of the hypopharynx are where squamous cell carcinoma arise:
pyriform sinus
postcricoid region
posterior wall
