 The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells, whose main function is to store calcium ions (Ca2+).
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells, whose main function is to store calcium ions (Ca2+).
Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant, with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10,000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the cell.
Small increases in calcium ions within the cell are easily detected and can bring about important cellular changes as the calcium is said to be a second messenger.
Calcium is used to make calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate, two compounds that the body uses to make teeth and bones.
This means that too much calcium within the cells can lead to hardening or calcification of certain intracellular structures, including the mitochondria, leading to cell death.
It is vital that calcium ion levels are controlled tightly, and can be released into the cell when necessary and then removed from the cell.
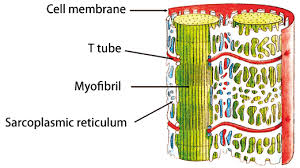
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules that extend throughout muscle cells, wrapping around the myofibrils contractile units of the cell.
Cardiac and skeletal muscle cells contain transverse tubules (T-tubules), which are extensions of the cell membrane that travel into the center of the cell.
T-tubules are closely associated with a specific region of the SR, known terminal cisternae sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle, with a distance of roughly 12 nanometers, separating them.
The terminal cisternae sarcoplasmic reticulum is the primary site of calcium release.
The SR contains membrane ion channel pumps, within its membrane that pump Ca2+ into the SR.
Calcium ion pumps use energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2 pumps are found primarily in cardiac and skeletal muscle.
The breakdown of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, along with the resultant release of calcium, is an important contributor to rigor mortis, the stiffening of muscles after death.
An increase in calcium concentration in the sarcoplasm can also cause muscle stiffness.
