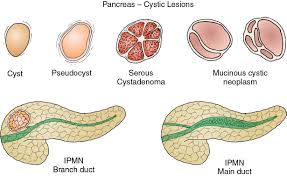
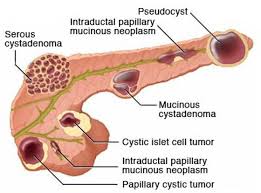
 Include benign serous cystadenomas, malignant cystadenomas, intraductal papillary mucinous tumors, inflammatory cysts and rarely cystic islet cell tumors and lymphoepithelial cysts.
Include benign serous cystadenomas, malignant cystadenomas, intraductal papillary mucinous tumors, inflammatory cysts and rarely cystic islet cell tumors and lymphoepithelial cysts.
Increasingly recognized, especially in asymptomatic and elderly patients due to the widespread use of high resolution imaging.
The incidence is estimated to be between 3 and 15%.
In autopsy studies pancreatic cyst were found in greater than 24% of autopsy cases.
Pancreatic cysts are detected in 3% of abdominal CT scans and 20% of abdominal MRI scans.
Prevalence increases with age, with up to 10 – 40% of patients having pancreatic cysts over 80 years of age.
In a Korean study intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm accounted for 41% of lesions, mucinous cystic neoplasms for 25.2%, solid pseudopapillary neoplasms for 18.3%, serious cystic neoplasms for 15.2% and others for 0.3 percent of pancreatic cysts (Yoon WJ).
In a Japanese study the expected mortality observed for pancreatic cancer was 22.5 times higher in patients with pancreatic cysts then the general Japanese population (Tada M).
In a American Gastroenterological Association review of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts reported estimated incident risk of malignant tumor of the incidental pancreatic cyst at 0.24% per year with a prevalent more risk of 25% at the time of diagnosis (Sheiman JM).
Information indicates pancreatic cyst can be asymptomatic at the initial presentation, but they may develop into cancer, and malignant tumor risk is higher in patients with pancreatic cyst than in the healthy population without such pancreatic cysts.
Pancreatic cysts are broadly classified as either non neoplastic or pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
Classified as true cysts or pseudocysts based on whether an epithelial lining is present or not.
Non neoplastic pancreatic cysts are better characterized as non epithelial type with pancreatic pseudocysts the most common, and epithelial cysts with retention cysts being the most common.
Non neoplastic cysts of the pancreas are benign without malignant potential, but they may be indistinguishable from pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
Non neoplastic cysts of the pancreas are rare, they should be recognized to avoid unnecessary pancreatic resection.
Non epithelial cysts include pancreatic pseudocysys and infectious related cysts, whereas epithelial cysts include retention cysts.
Pancreatic cystic neoplasms are mainly divided into mucinous and nonmucinous cystic lesions.
Pseudocysts account for 75% of pancreas cysts with true cysts making up 25% of such lesions.
