 The palate in the mouth refers to the roof of the oral cavity.
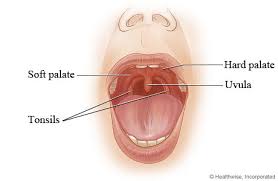
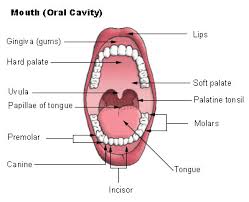
The palate in the mouth refers to the roof of the oral cavity.
The palate is divided into two parts: the hard palate and the soft palate.
The hard palate is the firm, bony area located in the front part of the mouth, closer to the front teeth.
It helps with speech articulation and plays a role in chewing and swallowing food.
The soft palate is located behind the hard palate and is composed of soft, flexible tissue.
It extends further back and ends with a small, finger-like projection, the uvula.
The soft palate and uvula help to close off the nasal passage during swallowing, preventing food and liquid from entering the nasal cavity.
The hard and soft palate contribute to the sense of taste enabling the detection of different flavors.
These taste buds sense sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami (savory) tastes.
The palate plays a role in the perception of textures and temperature of food.
The roof of the mouth, and the tongue, help us to appreciate the overall sensory experience of eating.
