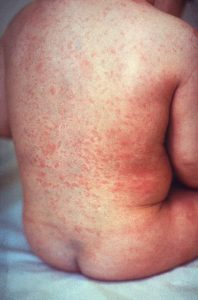
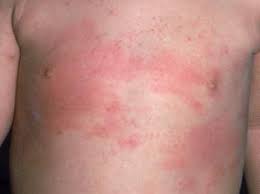
 An exanthem is a widespread skin rash and usually occurring in children.
An exanthem is a widespread skin rash and usually occurring in children.
An exanthem can be caused by toxins, drugs, or microorganisms, or can result from autoimmune disease.
Infectious exanthems
Of these six classical infectious childhood exanthems, four are viral.
Measles (rubeola)=‘first disease” measles virus erythematous macules and papules appear first on the head and spread down over body over 3 days.
In measles, a morbilliform rash lesions usually appear in the head and neck before spreading to the torso, and the rest of the body.
Enanthem: pathognomonic Koplik spots, punctate blue-white erosions occur on buccal mucosa.
Rubella, German measles identified, third disease, rubella virus
Pink macules and papules that appear first on the head and spread down over body in 24 hours.
Rash disappears in 2-3 days.
Enanthem: Forcheimmer sign, punctate petechiae on soft palate or uvula).
Erythema infectiosum,”fifth disease”
parvovirus B19
Confluent erythematous and edematous patches on cheeks (“slapped cheek”) for 1-4 days followed by a “lacy,” reticular, erythematous rash on the body.
Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum) #sixth disease”
HHV-6 and HHV-7
Rapid onset of erythematous, blanching macules and papules surrounded by white halos on the trunk after 3-5 days of high fever.
The rash spreads to the neck and body extremities and lasts 1-2 days.
Scarlet fever, or “second disease”, is associated with the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes.
Other common viruses can also produce an exanthem as part of their presentation.
Varicella zoster virus (chickenpox or shingles)
Herpes disaster, characterized by a single or multiple crops of vesicles that are usually limited to a single dermatome, and they development is preceded by pain and burning.
Mumps
rhinovirus (the common cold)
Some types of viral haemorrhagic fever
Tick-borne diseases like Rocky Mountain spotted fever produce a rash that may become extensive enough so as to be classified as exanthemous in as many as 90% of children with the disease.
Hand, foot, and mouth, disease and herpangina are associated with Coxsackie virus.
Coxsackievirus exanthem is associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease with numb for macularpapular or vascular lesions in the hands and feet that rarely spread centripetally.
Covid=19 causes macular, papular and papillary vascular rashes, acral lesions, vascular necrosis, purple petechiae, and lived-like rashes.
