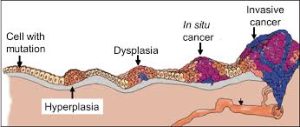
 Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells with varying potential to become malignant.
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells with varying potential to become malignant.
Some classify CIS as pre-cancer or a non-invasive form of cancer.
These abnormal cells grow in their normal place, remaining “in situ”.
Carcinoma in situ of the skin, is the accumulation of dysplastic epidermal cells within the epidermis only, that has failed to penetrate into the deeper dermis.
CIS usually does not form a tumor.
CIS lesions are flat as in the skin, cervix, or follows the existing architecture of the organ as in the breast, and lung.
CIS lesions of the colon, polyps, the bladder or the breast with ductal carcinoma in situ or lobular carcinoma in situ are tumoral like.
Many forms of CIS have a high probability of progression into cancer.
However, progression of CIS is known to be highly variable and not all CIS becomes invasive cancer.
In the TNM classification, carcinoma in situ is reported as TisN0M0 (stage 0).
Dysplasia is the earliest form of precancerous lesion recognizable in a biopsy, and it can be low-grade or high-grade.
High-grade dysplasia may also be referred to as carcinoma in situ.
High-grade dysplasia/carcinoma in situ in the uterine cervix can progress to invasive cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the cervix.
Cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL), previously called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), is a form of dysplasia that can progress to cervical cancer.
The term carcinoma in situ may be used interchangeably with high-grade SIL.
Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast is the most common precancer in women.
Bowen’s disease is a squamous carcinoma in situ of the skin.
Colon polyps often contain areas of CIS that will almost always transform into colon cancer if left untreated.
High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is equivalent to CIS of the prostate.
Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) of the lung is the only form of CIS that can kill directly: its pneumonic form can expand greatly and fill the lungs, preventing breathing and causing other dire effects on the host.
