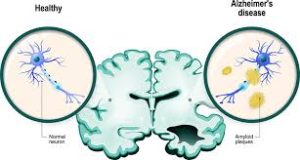
Amyloid beta (Aβ) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
The peptides are derived from the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP).
The gene for the amyloid precursor protein is located on chromosome 21.
Aβ molecules can aggregate to form flexible soluble oligomers which exists in several forms.
Misfolded oligomers can induce other Aβ molecules to also take the misfolded oligomeric form, leading to a chain reaction .
The oligomers are toxic to nerve cells.
The other protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, is tau protein,.
Tau protein forms such prion-like misfolded oligomers, as well, and and there is evidence that misfolded Aβ can induce tau to misfold.
The normal function of Aβ is not understood.
The absence of Aβ does not lead to any obvious loss of physiological function.
Potential activities discovered for Aβ, include; activation of kinase enzymes, protection against oxidative stress, regulation of cholesterol transport, functioning as a transcription factor, and anti-microbial activity.
The glymphatic system clears metabolic waste from the brain, and in particular amyloid beta: the significance of the glymphatic system in Aβ clearance in Alzheimer’s disease is unknown.
In healthy, young people 8.3% of total β-amyloid is cleared each hour via the CSF
A number of proteases are responsible for the recognition and degradation of amyloid beta; these include insulin degrading enzyme and presequence protease.
The rate of removal of amyloid beta is significantly increased during sleep.
Aβ is the main component of amyloid plaques, extracellular deposits found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Aβ can also form the deposits that line cerebral blood vessels in cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Amyloid plaques are composed of a tangle of Aβ oligomers and regularly ordered aggregates called amyloid fibrils, a protein fold shared by other peptides such as the prions associated with protein misfolding disease, also known as proteinopathy.
Soluble oligomeric forms of the amyloid beta may be causative agents in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
It is generally believed that Aβ oligomers are the most toxic, and play a central role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Brain Aβ is elevated in people with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.
Aβ is the main constituent of brain parenchymal and vascular amyloid; it contributes to cerebrovascular lesions and is neurotoxic.
It is still I known how Aβ accumulates in the central nervous system and initiates the disease of cells.
Aβ circulates in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and brain interstitial fluid (ISF) mainly as soluble Aβ40.
Amyloid plaques contain both Aβ40 and Aβ42, while vascular amyloid is predominantly the shorter Aβ40.
Increases in either total Aβ levels or the relative concentration of both Aβ40 and Aβ42 have been implicated in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.
Aβ40 is more concentrated in cerebrovascular plaques and Aβ42
in neuritic plaques.
All cancers are shown to be associated positively with increased Aβ levels, particularly hepatic cancers.
Adults with Down syndrome have accumulation of amyloid in association with evidence of Alzheimer’s disease, including declines in cognitive functioning, memory, fine motor movements, executive functioning, and visuospatial skills.
Autosomal-dominant mutations in APP cause hereditary early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, accounting for no more than 10% of all cases.
The vast majority of AD is not accompanied by such mutations.
Familial Alzheimer’s disease is likely to result from altered proteolytic processing.
Many mutations that lead to familial AD occur near γ-secretase cleavage sites on APP.
A common familial AD mutation at codon 717 of the APP gene, results in a valine to isoleucine amino acid substitution.
The APP V717I mutation has revealed extensive Aβ pathology throughout neuroaxis as well as widespread cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
The gene for the amyloid precursor protein is located on chromosome 21, and accordingly people with Down syndrome have a very high incidence of Alzheimer’s disease.
Imaging compounds, can selectively bind to amyloid beta in vitro and in vivo, and when combined with PET imaging, is used to image areas of plaque deposits in those with Alzheimer’s.
Amyloid beta can be measured semiquantitatively with immunostaining.
Amyloid beta may be primarily vascular, as in cerebral amyloid angiopathy, or in amyloid plaques in white matter.
ELISA, an immunosorbent assay which utilizes a pair of antibodies that recognize amyloid beta.
Vibrational microspectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules in tissue samples, and amyloid proteins like Aβ can be detected with this technique because of their high content of β-sheet structures.
Dual polarization interferometry is an optical technique which can measure early stages of aggregation by measuring the molecular size and densities as the fibrils elongate.
