 Inner ear abnormality that is common among adults with such impairment being present in 35% of Americans 40 years or older, corresponding to 69 million individuals.
Inner ear abnormality that is common among adults with such impairment being present in 35% of Americans 40 years or older, corresponding to 69 million individuals.
Approximately 1.8 million adults globally have severe bilateral vestibular hypofunction resulting in chronic disease equilibrium, postural instability, oscillopsia, and unsteady gait due to the failure of vestibular reflexes that stabilize the eyes, head, and body.
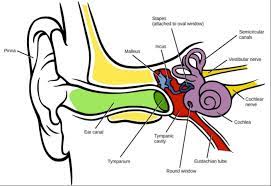
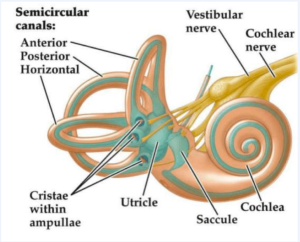
The vestibular system is integral to balance control and paired vestibular organs house within the temporal bone includes 3-semicircular canals, and two otolith organs.
Patients with bilateral vestibulo hypofunction have health related quality-of-life issues similar to those with severe bilateral hearing loss or renal insufficiency.
The semicircular canals are superior, posterior, and horizontal.
The otolith organs are the utricle and saccule, and they supply continuous input to the brain about rotational and translational head motion and provide orientation relative to gravity.
Otolith organs provide information to maintain gaze and postural stability via the vestibular-ocular reflex and the vestibulo-spinal reflex, respectively.
Typically related to vertigo and impaired balance owing to the disturbances in gaze and spinal stability.
Prevalence increases with age.
More common in the less educated and in patients with diabetes.
Associated with a 12 fold increase in the risk of falling.
Ranks among the leading causes of death among older individuals as it is associated with falls.
Patients should perform vestibular rehabilitation exercises, avoid ototoxic medications and sedating medications, and avoid activities that increase the risk of injury.
Testing for vestibular dysfunction involves electronystamography, caloric reflex test and assessment of postural function.
Evaluation of the National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys of U.S. adults 40 years and older revealed 35.4% of individuls had vestibular dysfunction (Agrawal Y).
A significant number of patients have vestibular dysfunction with testing, yet they have no complaints of dizziness.
Individuals withour a history of dizziness but who have abnormal postural assessment have an increaed odds of falling, indicating subclinical vestibular dusfunction is clinically significant.
Caloric reflex testing evaluates function of the horizontal semicircular canals.
The vestibular-ocular reflex and caloric reflex testing assess peripheral vestibular function.
Patients with vestibular dysfunction are signficantly more likely to have hearing loss, suggesting peripheral vestibular structures share a common blood supply and vulnerabilities wot degenerative disease, ischemia, trauma and to toxic agents.
Vestibular prostheses exist there are modified cochlear implants using electrodes to electrically stimulate branches of the vestibular nerve to convey information regarding body motion and orientation to reduce postural instability.
