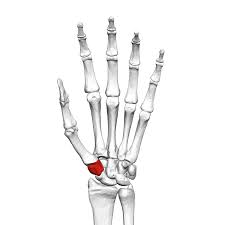
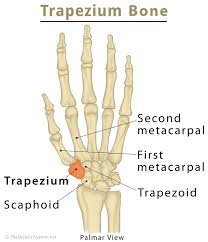
The trapezium bone, the greater multangular bone, is a carpal bone in the hand.
It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.
The trapezium is distinguished by a deep groove on its anterior surface.
The trapezium is situated at the radial side of the carpus, between the scaphoid and the first metacarpal bone of the thumb.
The trapezium is an irregular-shaped carpal bone found within the hand within the distal row of carpal bones, and is directly adjacent to the metacarpal bone of the thumb.
On its ulnar surface are found the trapezoid and scaphoid bones.
The superior surface is directed upward and medialward
Medially it is smooth, and articulates with the scaphoid.
Laterally it is rough and continuous with the lateral surface.
The inferior surface is oval, concave from side to side, convex from before backward, so as to form a saddle-shaped surface for articulation with the base of the first metacarpal bone.
This saddle-shaped articulation is partially responsible for the thumb’s opposable motion.
The dorsal surface is smooth.
The palmar surface is narrow and rough, it transmits the tendon of the Flexor carpi radialis, and is bounded laterally by an oblique ridge.
This surface gives origin to the Opponens pollicis and to the Abductor and Flexor pollicis brevis.
It also affords attachment to the transverse carpal ligament.
The lateral surface is for the attachment of ligaments.
The trapezium bone is one of the small bones found in the wrist, specifically in the carpal region.
It is situated at the base of the thumb, connecting to the metacarpal bone of the thumb and forming part of the thumb joint.
The trapezium bone contributes to the mobility and stability of the wrist and thumb, allowing for various movements and functions such as grasping, gripping, and pinch actions.
The tubercle of trapezium is found on the anterior surface of the bone.
It is where sometimes abductor pollicis brevis muscle attaches.
The carpal bones function as a unit to provide a bony superstructure for the hand.
The trapezium is the most radial of the bones surrounding the carpal tunne.
It is important in thumb movement.
The trapezium is susceptible to arthritis at the joint with the metacarpal bone of the thumb, due to overuse.
Trapezium
The trapezium bone, the greater multangular bone, is a carpal bone in the hand.
It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.
The trapezium is distinguished by a deep groove on its anterior surface.
The trapezium is situated at the radial side of the carpus, between the scaphoid and the first metacarpal bone of the thumb.
The trapezium is an irregular-shaped carpal bone found within the hand within the distal row of carpal bones, and is directly adjacent to the metacarpal bone of the thumb.
On its ulnar surface are found the trapezoid and scaphoid bones.
The superior surface is directed upward and medialward
Medially it is smooth, and articulates with the scaphoid.
Laterally it is rough and continuous with the lateral surface.
The inferior surface is oval, concave from side to side, convex from before backward, so as to form a saddle-shaped surface for articulation with the base of the first metacarpal bone.
This saddle-shaped articulation is partially responsible for the thumb’s opposable motion.
The dorsal surface is smooth.
The palmar surface is narrow and rough, it transmits the tendon of the Flexor carpi radialis, and is bounded laterally by an oblique ridge.
This surface gives origin to the Opponens pollicis and to the Abductor and Flexor pollicis brevis.
It also affords attachment to the transverse carpal ligament.
The lateral surface is for the attachment of ligaments.
The trapezium bone is one of the small bones found in the wrist, specifically in the carpal region.
It is situated at the base of the thumb, connecting to the metacarpal bone of the thumb and forming part of the thumb joint.
The trapezium bone contributes to the mobility and stability of the wrist and thumb, allowing for various movements and functions such as grasping, gripping, and pinch actions.
The tubercle of trapezium is found on the anterior surface of the bone.
It is where sometimes abductor pollicis brevis muscle attaches.
The carpal bones function as a unit to provide a bony superstructure for the hand.
The trapezium is the most radial of the bones surrounding the carpal tunne.
It is important in thumb movement.
The trapezium is susceptible to arthritis at the joint with the metacarpal bone of the thumb, due to overuse.
