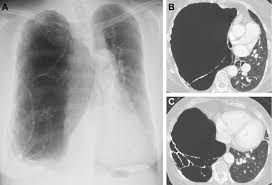
Swyer–James syndrome is a disease of the lungs, characterized by a small lung or part of lung.
Typical symptoms are of recurrent respiratory tract infections, but some have no symptoms.
Sometimes patients have shortness of breath on exertion, wheeze, reduced ability to exercise, cough, chest pain.
Cause by childhood bronchiolitis obliterans, typically following adenovirus infection, there is a reduction in blood vessels and overextended alveoli, resulting in air trapping in one or part of one lung.
It is rare.
It is a manifestation of postinfectious obliterative bronchiolitis.
In SJS, the involved lung or portion of the lung does not grow normally and is slightly smaller than the opposite lung.
Characteristic radiographic appearance is that of pulmonary hyperlucency, caused by overdistention of the alveoli in conjunction with diminished arterial flow.
Linked to adenovirus type 21 infection.
Swyer–James normally leaves shadowing in a CT scan in the upper lobar regions of one or both lungs.
The prognosis is good for sufferers of the illness to lead normal and healthy lives.
