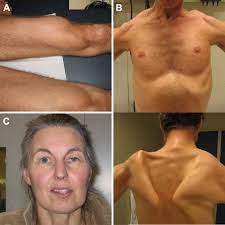
 A rare autosomal recessive progressive neuromuscular disease.
A rare autosomal recessive progressive neuromuscular disease.
A metabolic myopathy caused by a deficiency of acid alpha glucosidase, an enzyme that degrades lysosomal glycogen.
Characterized by progressive muscle weakness and loss of respiratory function, leading to early death.
In the classic infantile form glycogen is deposited in the heart, skeletal and respiratory muscles causing severe cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, and respiratory failure, leading to death within the first year of life.
In children and adults the disease is variability in disease progression.
Most deaths due to respiratory failure.
Treatment with enzyme replacement therapy with alglucosidase alfa.
Infants treated with alglucosidase alfa have improvement in survival and motor outcomes and use in children 8 years or older was associated with improved walking and stabilization in pulmonary functionover 18 months (van der Ploeg AT).
Avalglucosidase approved based on the results of a randomized phase 3 trial manifesting improved six minute walking tests.
