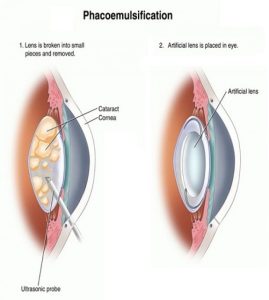
 Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgical technique in which the eye’s internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye.
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgical technique in which the eye’s internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye.
The aspirated fluid is replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the anterior chamber.
Topical anesthesia is most commonly employed, typically by the instillation of a local anesthetic such as tetracaine or lidocaine.
Anesthetic may be injected into the area surrounding or behind the eye muscle cone to more fully immobilize the extraocular muscles and minimize pain sensation.
A facial nerve block using lidocaine and bupivacaine may occasionally be performed to reduce lid squeezing.
General anesthesia is recommended for children, or those with traumatic eye injuries with cataract, for very apprehensive or uncooperative patients.
Cardiovascular monitoring is mandatory with the use of general anesthesia.
Proper sterile precautions are utilized throughout the procedure.
An eye speculum is inserted to keep the eyelids open.
Phacoemulsification is performed, after incisions are made in the eye to allow the introduction of surgical instruments.
The anterior face of the capsule that contains the lens inside the eye is removed.
Phacoemulsification surgery involves the use of a microprocessor with controlled fluid dynamics.
The phaco probe is an ultrasonic handpiece with a titanium or steel needle.
The needle vibrates at ultrasonic frequency to sculpt and emulsify the cataract
Its pump aspirates particles through the tip.
The cataract is usually broken into two or four pieces and each piece is emulsified and aspirated out with suction.
After removing all hard central lens nucleus with phacoemulsification, the outer lens cortex is removed with
suction.
The posterior capsule remains intact.
An intraocular lens implant is placed into the remaining lens capsule.
It is placed in the posterior chamber in the capsular bag.
Because a smaller incision is required, few or no stitches are needed and the patient’s recovery time is usually shorter when using a foldable IOL.
Use of ultrasound in phacoemulsification can cause effects such as corneal edema, and macular edema after surgery.
Macular edema in phacoemulsification is caused intraocular pressure fluctuation during surgery, creating micro bubbles and generate micro emboli in macular vessels that can cause micro ischemia in the retinal nerve fiber layer.
A Cochrane Review found that
eyes that underwent combined glaucoma and phacoemulsification surgery had a significantly lower intraocular pressure (-1.62 mmHg) compared to eyes that underwent phacoemulsification cataract surgery alone.
A Cochrane Review of 16 trials comparing the effectiveness of laser assisted cataract surgery with standard ultrasound phacoemulsification found no significant differences between the two techniques in terms of visual or refractive outcomes or overall complications.
