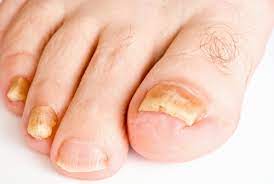
 Onychomycosis, a fungal infection which predominantly affects toenails.
Onychomycosis, a fungal infection which predominantly affects toenails.
Incidence about 13% and almost 50% in adults over the age of 70 years.
Affects approximately 35 million people in the US.
Incidence increases with age.
Less than 1% of individuals under the age of 19 affected while 18% aged 60-79 years have the disorder.
More common in men.
Risk factors include psoriasis immunosuppression, and positive family history.
Accounts for 50% of nail diseases.
Toenails more commonly involved than fingernails.
Increased risk with diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, presence of HIV infection and in individuals older than 60 years.
The risk of developing infection increases with nail trauma, tinea pedis and psoriasis.
Risk factor for cellulitis as it provides a portal of entry for bacteria.
In diabetics can lead to foot infections, ulcers and gangrene.
90% of cases caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes and the remainder of cases caused by yeasts (Candida) and molds.
Common signs and symptoms include nail discolouration and thickening, nail separation from nail bed, and nail brittleness.
Estimated prevalence of onychomycosis in North America is between 8.7% to 13.8%.
Only rarely associated with candida.
4 categories of disease: superficial, proximal subungual, distal subungual and total dystrophic.
Distal subungual form the most common accounting for 75-85% of cases.
Distal type associated with thickened and friable changes of the nails, subungual hyperkeratosis and nail discoloration.
Total dystrophic for affects the entire nail.
The nail may be pigmented in distal subungual disease.
Differential diagnosis includes psoriasis, lichen planus, and eczema.
PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) stain of a nail clipping is the most specific and sensitive test for diagnosis.
Treatment with terbinafine (Lamisil) 250 mg/day for 3 months or itraconazole (Sporanox) 400 mg/day for 1 week every 4 weeks, for 12 weeks or fluconazole (Diflucan) 400 mg weekly for 48 weeks.
Tavaborole topical solution 5% (Kerydin) approved for the treatment of onchomycosis of the toenails.
Tavaborole is an alcohol-based solution that can be applied with the dropper to the infected toenail once daily for 48 weeks.
Tavaborole use does not require debridement of the nail and results in 6.5-9.1% complete cure at 52 weeks.
Tavaborole side effects occur in about 1% of patients and include application site exfoliation, application site erythema, application site dermatitis, and ingrown toenails.
