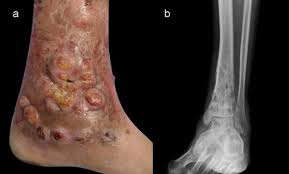
 Mycetoma is a chronic infection in the skin caused by either bacteria (actinomycetoma) or fungi (eumycetoma), typically resulting in a triad of painless firm skin lumps, the formation of weeping sinuses, and a discharge that contains grains.
Mycetoma is a chronic infection in the skin caused by either bacteria (actinomycetoma) or fungi (eumycetoma), typically resulting in a triad of painless firm skin lumps, the formation of weeping sinuses, and a discharge that contains grains.
It is a neglected tropical disease.
80% occur in feet.
Clinical triad: painless firm skin lump, multiple weeping sinuses, grainy discharge.
Infection is caused as a result of localized skin trauma, such as stepping on a needle or wood splinter, or through a pre-existing wound.
Usual onset is slowly progressive.
Types of mycetoma:
Actinomycetoma (bacterial)
Eumycetoma (fungal)
Diagnostic methods
Ultrasound, fine needle aspiration
Most eumycetoma is caused by M. mycetomatis, whereas most actinomycetoma is caused by N. brasiliensis, S. somaliensis, A. madurae and Actinomadura pelletieri.
People who develop mycetoma likely have a weakened immune system.
Most cases of mycetoma occur in Sudan, Venezuela, Mexico, and India.
It appears most frequently in people living in rural areas, particularly in farmers and shepherds.
Most often reported in men between 20 and 40 years.
Misdiagnosed or delayed diagnosis of mycetoma osteomyelitis can result in amputation or radical resection.
Frequent exposure to penetrating wounds by thorns or splinters is a predisposing risk factor.
The risk i reduced by disinfecting wounds and wearing shoes.
Mycetoma are caused by common saprotrophs found in the soil and on thorny shrubs in semi-desert climates.
Causative agents include:
Madurella mycetomatis (fungus)
Nocardia brasiliensis (bacteria)
Actinomadure madura (bacteria)
Streptomyces somaliensis (bacteria)
Actinomadura pelletieri (bacteria)
Typically begins as a painless swelling beneath the skin, which over several years grows to become a lump.
Massive swelling and induration of the area may occur, in addition to skin rupture and the formation of sinus tracts.
The lesions may discharge pus and grains filled with organisms.
The underlying bone may be affected.
Diagnosis: through microscopic examination of the grains in the nodule and by culture.
The bacterial form and the fungal forms of mycetoma infection of the foot share similar clinical and radiological features.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a very valuable diagnostic tool.
Treatment:
Itraconazole is used for the treatment of mycetoma.
Actinomycetoma, the bacterial form, can be cured with antibiotics.
Eumycetoma, the fungal form, is treated with antifungals.
Surgery in the form of bone resection may be necessary in late presenting cases.
In advanced cases, amputation is another surgical treatment option.
