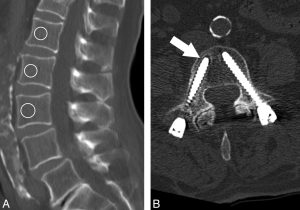
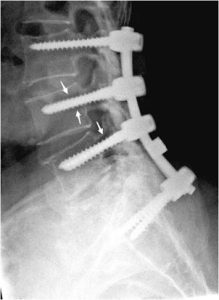
 Causes of screw loosening after spinal fusion include, poor bone quality, poor healing, improper screw fixation, and excessive impact on the screws.
Causes of screw loosening after spinal fusion include, poor bone quality, poor healing, improper screw fixation, and excessive impact on the screws.
Excess impact on the screws after spinal fusion can result from high-impact physical activity, poor posture, and a sedentary lifestyle.
High-impact activities or activities that involve intensely bending or twisting the spine may result in fusion hardware failure as a result.
Poor healing or failed fusion can cause the pedicle screws and other hardware to loosen.
Failed fusion occurs when the bone graft doesn’t successfully merge the vertebrae into a single bone.
Certain factors can increase your risk of pedicle screw loosening after spinal fusion, including:
Diabetes
Older age
Low bone density
Patients with low bone density due to fracture, osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other medical conditions, are at an increased risk of loosening screws after spinal fusion.
Screws can also simply loosen after spinal fusion with time, as they undergo normal wear and tear.
Older patients may not experience the effects of wear and tear on the screws, but younger patients will likely develop symptoms at some point.
When screws loosen, they can irritate the neighboring nerves and tissue, causing pain, neurological symptoms, and crepitus.
New or recurrent back pain after spinal fusion may be a result of pedicle screw loosening can indicate failed spinal fusion )failed back surgery syndrome).
Many patients require re-operation for pain management.
Symptoms of failed spinal fusion include:
Limited spinal mobility
Spasms in the back
Insomnia
Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities
Persistent back pain
Non-surgical treatment measures:
Epidural steroid injections, physical therapy, and radiofrequency ablation, among other techniques, are non-surgical options for failed spinal fusion.
Spinal fusion alternatives include dynamic stabilization systems, IDET, and stem cell therapy.
Intradiscal Electrothermal Coagulation (IDET) involves inserting a needle into the affected disc area, and application of gentle heat to the exterior of the intervertebral disc.
This process helps strengthen and thicken the collagen fibers in the disc exterior, potentially offering relief from chronic back pain.
Dynamic stabilization systems can replace spinal fusion after lumbar spinal decompression surgery.
This type of surgical implant stabilizes the spine without permanently limiting its motion.
