 Results from a surfactant deficiency.
Results from a surfactant deficiency.
Known as respiratory distress syndrome and is one of the most common problems associated with prematurity.
Course dependent upon the size and gestational age of the newborn.
Surfactant made by airway cells and consists of phospholipids and protein.
Surfactant is produced beginning about the 24th week of gestation and is found in amniotic fluid between 28-32 weeks.
By week 35 most infants have sufficient amounts of surfactant.
Surfactant normally released into lung tissues lowering surface tension in the airways keeping lung alveoli open.
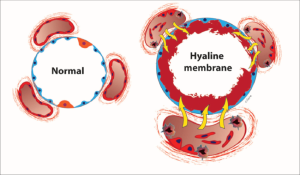
A pulmonary surfactant-deficient lung is characterized by collapsed air spaces alternating with hyperexpanded areas, vascular congestion, and, eventually hyaline membranes.
Hyaline membranes are composed of fibrin, cellular debris, red blood cells, rare neutrophils and macrophages.
Alveoli collapse when surfactant is insufficient and damaged cells collect in the airways and further affect the ability to breathe.
The damaged cells are referred to as hyaline membranes.
As lung function decreases oxygen levels decrease and carbon dioxide increases in the blood and can lead to acidosis and respiratory failure.
Occurs in more than half of babies born before age 28 weeks gestation, and in less than one third of babies born between 32 and 36 weeks.
