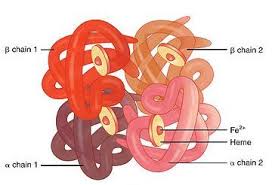
 A tetrameric protein composed of two pairs of globin chains, each with its own heme group.
A tetrameric protein composed of two pairs of globin chains, each with its own heme group.
Normally, people have four functional alpha globin genes and two functional beta globin genes that regulate the manufacture of the proteins that form adult hemoglobin(HbA or a2B2).
Hemoglobin tetramer is encoded by multi gene clusters on chromosome 16 for alpha and 11 for beta chains, respectively.
2 Alpha globin proteins combine with two beta globin proteins, and each of the four carries a heme group.
Normal adult red blood cells contain HbA(a2b2) with small amounts of HbA2 (a2d2), and fetal hemoglobin (a2g2).
Normal limits for hemoglobin values for women is 12.-16.0g/dL and for men 14.0-18.0g/dL.
In the absence of any disease, females typically have about a 10% lower hemoglobin concentration than males of similar size and stature.
Approximately 97% of normal hemoglobin in adults consists of alpha-globin and beta-globin chains.
About 98.5% of the oxygen in a sample of arterial blood in a healthy human, breathing air at sea-level pressure, is chemically combined with hemoglobin molecules.
About 1.5% is physically dissolved in the other blood liquids and not connected to hemoglobin.
The hemoglobin molecule is the primary transporter of oxygen
Age, sex, and pregnancy status, environmental factors such as smoking and altitude affect hemoglobin concentration.
Normal hemoglobin levels in women and black men are 1-2 g/dL less than in Caucasian men.
Level along with hematocrit and mean corpuscular volume are lower in blacks than in whites
Synthesis controlled by the alpha-like globin cluster on chromosome 16 and the beta-like globin cluster on chromosome 11 producing embryonic and adult hemoglobin.
Enhancer elements on chromosome 11 termed the ß locus control region and upstream (5’) of ß locus structural genes.
The ε-globin gene is the most 5’ globin structural gene and is active in fetal life.
γ-globin genes Gγ and Aγ are the major B like genes expressed in most of fetal life.
The δ and ß globin genes are activated in late fetal life.
ß globin gene is not highly expressed in red blood cells after birth and in adults.
Clinically significant hemoglobinopathies arise from mutations in the ß globin gene.
α-globin is the other major globin locus on chromosome 16.
α-globin gene expression begins in early fetal life and continues through adulthood.
More than 1000 naturally occurring inherited mutations of either the structure or synthesis of the alpha and beta-like globin chains.
Hemoglobin (Hb) is the primary vehicle for transporting oxygen in the blood.
Oxygen is also carried dissolved in the blood’s plasma, but to a much lesser degree than in hemoglobin.
Oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in RBCs is released into the blood’s plasma and absorbed into the tissues.
Each hemoglobin molecule has the capacity to carry four oxygen molecules, and these molecules of oxygen bind to the iron of the heme group.
Hemoglobin contains four heme groups each capable of reversibly binding to one oxygen molecule.
The binding of the first oxygen molecule induces a conformational change of hemoglobin that increases the affinity for the remaining three oxygen molecules.
The capacity of hemoglobin that is filled by oxygen at any time is called the oxygen saturation.
Expressed as a percentage, the oxygen saturation is the ratio of the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin, to the oxygen-carrying capacity of the hemoglobin.
The oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin is determined by the type of hemoglobin present in the blood.
