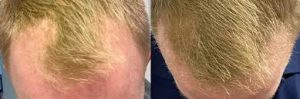
 Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, to a bald or balding part of the body known as the recipient site.
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, to a bald or balding part of the body known as the recipient site.
Hair transplantation is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness.
It is a minimally invasive procedure.
Grafts containing hair follicles that are genetically resistant to balding (are transplanted to the bald scalp.
Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, pubic hair and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants.
Hair grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis surrounding the hair follicle.
Many tiny grafts are transplanted rather than a single strip of skin.
Hair naturally grows in groupings of 1 to 4 hairs, and current techniques harvest and transplant hair follicular units in their natural groupings: (follicular unit transplantation (FUT).
Hair transplantation achieves a natural appearance by mimicking original hair orientation.
Donor hair can be harvested in two different ways: strip harvesting, and follicular unit extraction.
Folliscopy preoperatively identifies
w the existing density of hair, so that postoperative results of newly transplanted hair grafts can be accurately assessed.
Some patients benefit with preoperative topical minoxidil application and vitamins.
Prior to surgery using any medicines which might result in intraoperative bleeding and resultant poor grafting are eliminated.
Alcohol and smoking can contribute to poor graft survival.
Post operative antibiotics are commonly prescribed to prevent wound or graft infections.
Half transplant operations are performed on an outpatient basis, with mild sedation and injected local anesthesia.
The scalp is treated with an antibacterial agent prior to the donor scalp being harvested.
The proper extraction of the hair follicle is paramount to ensure the viability of the transplanted hair and avoid transection of the hair shaft from the hair follicle.
Hair follicles grow at a slight angle to the skin’s surface, so transplanted tissue must be removed at a corresponding angle.
Donor grafts are extracted by strip excision harvesting, and follicular unit extraction.
The most common technique for removing hair and follicles from a donor site is the Strip harvesting or follicular unit transplantation ( FUT.
A strip of skin from the posterior scalp is harvested in an area of good hair growth.
A single-, double-, or triple-bladed scalpel is used to remove strips of hair-bearing tissue from the donor site,with
intact hair follicles: closure follows.
The excised strip is about 1–1.5 x 15–30 cm in size.
Then dissection of individual follicular unit grafts, from the strip occurs with
binocular Stereo-microscopes.
Small micro blades or fine needles puncture the sites for receiving the grafts.
They are placed in a predetermined density and pattern, and angling the wounds in a consistent fashion to promote a realistic hair pattern.
Inserting the individual grafts in place then occurs.
Strip harvesting will leave a thin linear scar in the donor area.
It is typically covered by a patient’s hair even at relatively short lengths.
With Follicular Unit Extraction individual follicular units containing 1 to 4 hairs are removed under local anesthesia.
It typically uses tiny punches of between 0.6mm and 1.0mm in diameter.
Very small micro blades or fine needles puncture the sites for receiving the grafts, placing them in a predetermined density and pattern, and angling the wounds in a consistent fashion to promote a realistic hair pattern.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) procedure is more time-consuming than strip surgery.
The procedure can take anywhere from a couple hours to extract 200 grafts for a scar correction to a surgery over two consecutive days for a megasession of 2,500 to 3,000 grafts.
FUE advantage over strip harvesting is that FUE harvesting negates the need for large areas of scalp tissue to be harvested, so there is no linear incision on the back of the head and it doesn’t leave a linear scar.
Only small, punctate scars remain which are virtually not visible and any post-surgical pain and discomfort is minimized: no suture removal is required, recovery from Micro Grafting FUE is less than 7 days.
Disadvantages increased surgical times and higher cost to the patient.
Follicular unit extraction can lead to a lower ratio of successfully transplanted follicles as compared to strip harvesting.
Follicular unit transplant
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT) is the traditional hair transplant method which involves extracting a linear strip of hair bearing skin from the back or the side of the scalp.
The strip is then dissected to separate individual grafts.
Robotic hair restoration devices utilize cameras and robotic arms to assist the surgeon with the FUE procedure.
Applications for hair transplant surgery, include:
Androgenetic alopecia
Eyebrow transplant
Frontal hair line lowering or reconstruction
If donor hair numbers from the back of the head are insufficient, it is possible to perform body hair transplantation on appropriate candidates who have available donor hair on the chest, back, shoulders, torso and/or legs.
There is a natural difference in textural characteristics between body hair and scalp hair, and growth rates.
During the first ten days after transport some hairs are inevitably traumatized by their relocation, may fall out:is referred to as shock loss.
After two to three months new hair grows from the moved follicles, and then grow normally, and continue to thicken through the next six to nine months.
Shock loss is a common side effect of hair transplantation that is usually temporary.
Bald patches are also common, as fifty to a hundred hairs can be lost each day.
Post-operative hiccups have also been seen in around 4% of transplant patients.
Transplanted hair will only grow in its new site for as long as it would have in its original one.
The follicular unit hair transplant procedure has become more refined and minimally invasive as the size of the graft incisions have become smaller.
These smaller and less invasive incisions enable surgeons to place a larger number of follicular unit grafts into a given area.
Over 50 grafts can be placed per square centimeter, when appropriate for the patient.
The adoption of the “lateral slit” technique enabled hair transplant surgeons to orient 2 to 4 hair follicular unit grafts so that they splay out across the scalp’s surface.
This technique enabled the transplanted hair to lie better on the scalp and provide better coverage to the bald areas.
