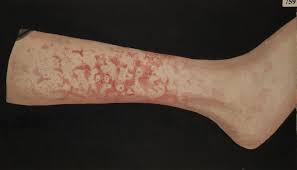
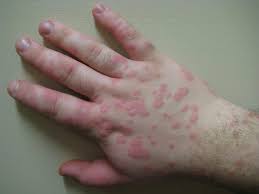
 Erythema marginatum is an acquired skin condition which primarily affects the arms, trunk, and legs.
Erythema marginatum is an acquired skin condition which primarily affects the arms, trunk, and legs.
It is a type of erythema characterized by bright pink or red circular lesions which have sharply-defined borders and faint central clearing.
The lesions typically range between 3-10cm in size, and are distributed symmetrically over the torso and inner surfaces of the limbs and extensor surfaces.
The condition is characterized by circular, non-pruritic, erythematous rashes which form on the trunk and extremities of the body.
The lesions last between one and four weeks but have been known to be present on patients for as long as several months.
An association with bradykinin has been proposed in the case of hereditary angioedema.
The rings lesions are barely raised and are non-itchy.
The face is generally spared with lesions.
The rash has a known serpiginous edge, and often appears and disappears spontaneously over time.
Histologically there is infiltration of mononuclear cells and neutrophils in the papillary and upper half of the reticular dermis layer.
It occurs in less than 10% of patients with acute rheumatic fever.
EM is considered a major Jones criterion when it does occur.
The four other major criteria of acute rheumatic fever include carditis, polyarthritis, Sydenham’s chorea, and subcutaneous nodules.
It is often associated with Group A streptococcal infection, otherwise known as Streptococcus pyogenes infection, which can be detected with an ASO titer.
It is an early feature of acute rheumatic fever though not diagnostic.
It is also a harbinger to or accompanies an attacks of angioedema.
It can be seen in conditions like allergic drug reactions, sepsis and glomerulonephritis.
The diagnosis of erythema marginatum can be made by examination of skin.
A skin biopsy may be performed if needed, to confirm the diagnosis.
Medical history and family history may also be taken into account.
Erythema marginatum can be treated with steroids.
When the condition is associated with ARF and severe carditis, corticosteroids are indicated , with a 10-day course of oral Penicillin.
