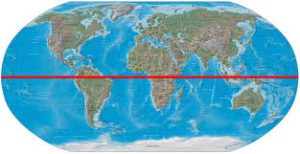
The equator is a circle of latitude, about 40,075 km (24,901 mi) in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
It is an imaginary line.
The equator is located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles.
It is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles.
On and near the equator noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead every day, year-round.
The equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throughout the year.
On the equinoxes, approximately March 20 and September 23,the subsolar point crosses Earth’s equator at a shallow angle, sunlight shines perpendicular to Earth’s axis of rotation, and all latitudes have nearly a 12-hour day and 12-hour night.
The equator is one of the five notable circles of latitude on Earth/
The other four are the two polar circles-the Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle-and the two tropical circles-the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
The equator is the only line of latitude which is also a circle—meaning, one whose plane passes through the center of the globe.
The plane of Earth’s equator, when projected outwards to the celestial sphere, defines the celestial equator.
In the cycle of Earth’s seasons, the equatorial plane runs through the Sun twice a year: on the equinoxes in March and September.
The Sun appears to travel along the equator at these times.
Locations on the equator experience the shortest sunrises and sunsets because the Sun’s daily path is nearly perpendicular to the horizon for most of the year.
The length of daylight from sunrise to sunset is almost constant throughout the year.
Daylight it is about 14 minutes longer than nighttime due to atmospheric refraction and the fact that sunrise begins, or sunset ends, as the upper limb, not the center, of the Sun’s disk contacts the horizon.
The earth bulges slightly at the equator; its average diameter is 12,742 km (7,918 mi), but the diameter at the equator is about 43 km (27 mi) greater than at the poles.
Sites near the equator are good locations for spaceports as they have the fastest rotational speed of any latitude, reducing the fuel needed to launch spacecraft eastward, the direction of Earth’s rotation.
The precise location of the equator is not truly fixed, as the true equatorial plane is perpendicular to the Earth’s rotation axis, which drifts about 9 metres (30 ft) during a year.
Geological samples show that the equator significantly changed positions million years ago.
The equatorial radius is 6,378.1366 km (3,963.1903 mi), but If it were really circular, the length of the equator would then be exactly 2π times the radius, namely 40,075.0142 km (24,901.4594 mi).
The equator passes through the land of 11 countries.
Indonesia straddles the greatest length of the equatorial line across both land and sea.
Regardless of the time of day the North Pole will be dark, and the South Pole will be illuminated.
Throughout the year, the Northern and Southern hemispheres are alternately turned either toward or away from the Sun, depending on Earth’s position in its orbit.
The hemisphere turned toward the Sun receives more sunlight and is in summer, while the other hemisphere receives less sun and is in winter.
Near the equator, the variation in the strength of solar radiation is different relative to the time of year than it is at higher latitudes:
The maximum solar radiation is received during the equinoxes, when a place at the equator is under the subsolar point at high noon, and the intermediate seasons of spring and autumn occur at higher latitudes.
The minimum solar radiation occurs during both solstices, when either pole is tilted towards or away from the sun, resulting in either summer or winter in both hemispheres.
Equinox
Time of the year when the sun is nearest to the equatorial plane giving equal lengths of day and night.
Solstice
Time of the year when the sun is farthest from the equatorial plane resulting in long nights and days.
An equinox occurs at the start of the spring and fall.
Occurs on March 20 (Vernal equinox) and on September 22 (Autumnal equinox).
The solstice occurs during the summer and the winter.
Occurs on June 21(Summer Solstice) and on Dec 22 (Winter Solstice).
The solstices result in a change of the length of night and day, the equinoxes do not.
The summer and winter solstices result in the longest and shortest day of the year respectively while the equinoxes result in an equal amount of daylight and darkness received all across the earth.
Near the equator, there is little temperature change throughout the year, though there may be marked differences in rainfall and humidity: summer, autumn, winter and spring terminology do not generally apply.
Lowlands around the equator generally have a tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate.
Average annual temperatures in equatorial lowlands are around 31 °C (88 °F) during the afternoon and 23 °C (73 °F) around sunrise.
Rainfall is very high away from cold ocean current upwelling zones, from 2,500 to 3,500 mm (100 to 140 in) per year, and are about 200 rainy days per year and average annual sunshine hours are around 2,000.
Some higher altitudes such as the Andes and Mount Kilimanjaro have glaciers.
This is slightly above the snow line and is the only place on the equator where snow lies on the ground.
At the equator, the snow line is around 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) lower than on Mount Everest and as much as 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) lower than the highest snow line in the world, near the Tropic of Capricorn on Llullaillaco.
