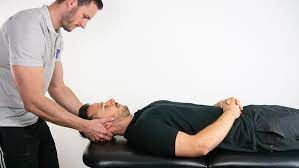
 A diagnostic test for the presence of cervical radiculopathy.
A diagnostic test for the presence of cervical radiculopathy.
The test is performed with the patient lying supine, with the neck in a comfortable position; the examiner securely grasps the patient’s either by placing each hand around the patient’s mastoid processes, while standing at their head, or place one hand on their forehead and the other on the occiput.
Applying a distraction force to the slightly flexed neck, the head is pulled to the examiner.
A positive cervical distraction test reduces or eliminates symptoms, and indicates nerve root compression and facet joint pressure.
This tests the neural foramen and joint capsules around the facet joints of the cervical spine.
The test secondarily observes the neck extensor muscles.
Grading the pressure is assessed by the amount of pressure and pain relieved while performing the test.
Due to aging the disc height decreases and bone spurs accumulate, and the space for nerves to enter and exit the vertebral canal gets smaller, resulting in greater pressure on the nerve roots causing pain and weakness.
With distraction, the joint space is increased relieving the pressure on the nerve roots, thus decreasing the symptoms.
It has a sensitivity: 0.44%, a specificity: 0.97% and a reliability of 0.88%.
