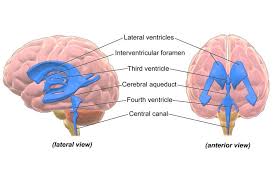
 The cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brain.
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brain.
The CA is located in the midbrain dorsal to the pons and ventral to the cerebellum.
The cerebral aqueduct is surrounded by an enclosing area of gray matter called the periaqueductal gray, or central gray.
The cerebral aqueduct, develops from the central canal of the neural tube, that is present in the developing mesencephalon.
It acts like a canal that passes through the midbrain.
It connects the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle so that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) moves between the cerebral ventricles and the canal connecting these ventricles.
Aqueductal stenosis, is the narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct, which obstructs the flow of CSF and has been associated with non-communicating hydrocephalus.
Aqueductal stenosis can be congenital, arise via tumor compression or through gliosis secondary to an initial partial obstruction.
