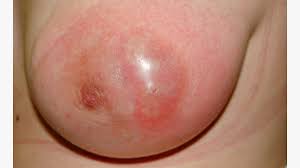
 A breast abscess is a painful, swollen lump that forms underneath the skin in the breast tissue.
A breast abscess is a painful, swollen lump that forms underneath the skin in the breast tissue.
It is usually caused by an infection, which may be bacterial or fungal in nature.
Breast abscesses are more common in women who are breastfeeding, but they can also occur in non-breastfeeding women and men.
The symptoms of a breast abscess can include pain, redness, warmth, swelling, and a discharge of pus from the skin.
Treatment for a breast abscess may involve antibiotics, pain medication, and drainage of the abscess.
Antibiotics are typically given to treat the infection and prevent it from spreading.
Pain medication may be prescribed to manage discomfort and make the patient more comfortable.
Drainage of the abscess with a small incision into the abscess to allow the pus to drain out.
An abscess in the breast may be treated by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration or by surgical incision and drainage; each of these approaches is performed under antibiotic coverage.
For small breast abscesses, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration such as to completely drain the abscess is widely recognized as a preferred initial management.
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the abscess completely, for larger or more severe abscesses that do not respond to antibiotics or drainage treatment.
Nonpuerperal breast abscesses have a higher rate of recurrence compared to puerperal breast abscesses.
There is a high statistical correlation of nonpuerperal breast abscess with diabetes mellitus.
