I
Early on, it may be asymptomatic.
Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move.
Complications may include collapse of the bone or nearby joint surface.
Osteonecrosis, also referred to as bone infarction, aseptic necrosis, ischemic bone necrosis.
Differential diagnosis;
Osteopetrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Legg–Calvé–Perthes syndrome, sickle cell disease
Frequency about 15,000 per year.
Avascular necrosis usually affects people between 30 and 50 years of age.
About 10,000 to 20,000 people develop avascular necrosis of the head of the femur in the US each year.
Risk factors include bone fractures, joint dislocations, alcoholism, and the use of high-dose steroids.
Additional risk factors include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and organ transplantation.
Osteonecrosis is also associated with cancer, lupus, sickle cell disease, HIV infection, Gaucher’s disease, and Caisson disease.
The condition may also occur without any clear reason.
The most commonly affected bone is the femur.
Avascular necrosis most commonly affects the ends of long bones such as the femur.
Other relatively common sites include the upper arm bone, knee, shoulder, ankle, and jaw.
Diagnosis is based on medical imaging such as X-ray, CT scan, or MRI.
Rarely biopsy may be used for diagnosis.
Treatments may include medication, not walking on the affected leg, stretching, and surgery.
Surgery is eventually required and may include core decompression, osteotomy, bone grafts, or joint replacement.
People 30 to 50 years old are most commonly affected.
Males are more commonly affected than females.
About half of cases show multiple sites of damage.
Bisphosphonates are associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Prolonged, repeated exposure to high pressures as experienced by commercial divers has been linked to AVN.
In children, avascular osteonecrosis can occur in the hip as part of Legg–Calvé–Perthes syndrome, and it can also occur as a result after malignancy treatment such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia and allotransplantation.
After reduction or removal of the blood supply, hematopoietic cells being most sensitive to low oxygen are the first to die usually within 12 hours, bone cells (osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts), die within 12–48 hours, and that bone marrow fat cells die within 5 days.
Following reperfusion, repair of bone occurs.
Repair occurs in 2 phases: angiogenesis and movement of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells from adjacent living bone tissue grow into the dead marrow spaces, as well as entry of macrophages that degrade dead cellular and fat debris.
Cellular differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts or fibroblasts.
It is possible for the remaining inorganic mineral volume to form a framework for establishment of new, fully functional bone tissue.
Diagnosis:
In the early stages, bone scintigraphy and MRI are the preferred diagnostic tools.
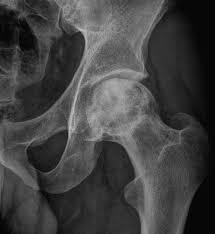
X-ray images of avascular necrosis in the early stages usually appear normal.
With later stage disease X-rays appear relatively more radio-opaque due to the nearby living bone becoming resorbed secondary to reactive hyperemia.
Necrotic bone itself does not show increased radiographic opacity, as dead bone cannot undergo bone resorption which is carried out by living osteoclasts.
Late radiographic findings include a radiolucency area following the collapse of subchondral bone and ringed regions of radiodensity resulting from saponification and calcification of marrow fat following medullary infarcts.
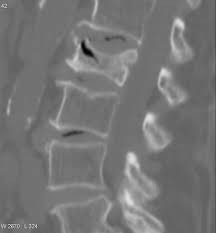
Avascular necrosis of a vertebral body after a vertebral compression fracture is called Kümmel’s disease, and is associated with the intravertebral vacuum cleft sign.
AVN of the scaphoid bone, navicular bone and lunate bone can occur.
Management:
The most common being the total hip replacement (THR).
Bisphosphonates which reduce the rate of bone breakdown may prevent collapse due to AVN.
Other treatments: core decompression, placement of living bone chip and an electrical device to stimulate new vascular growth, and the free vascular fibular graft (FVFG), in which a portion of the fibula, along with its blood supply, is removed and transplanted into the femoral head.
A Cochrane review found no improvement between people who have had hip core decompression and participate in physical therapy, versus physical therapy alone.
Avascular necrosis disability depends on which bone is affected, and how large an area is involved, and how effectively the bone rebuilds itself.
Normally, bone continuously breaks down and rebuilds as old bone is resorbed and replaced with new bone.
The process keeps the skeleton strong and helps it to maintain a balance of minerals.
With avascular necrosis, however, the healing process is usually ineffective and the bone tissues break down faster than the body can repair them.
As the disease progresses, the bone collapses, and the joint surface breaks down, leading to pain and arthritis.
