 An antibody is a glycosylated protein complex that is synthesized and secreted by immune B cells
An antibody is a glycosylated protein complex that is synthesized and secreted by immune B cells
Its formation is usually in response to the exposure of the immune system to a foreign or non-self molecule, such as an infectious agent, or transplanted tissue.
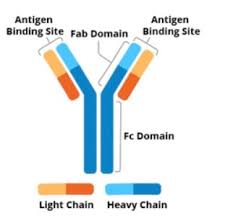
An antibody contains four polypeptide proteins chains: two heavy chains and two light chains.
The chains have variable domains, which bind the target antigen and constant domains, which mediate events downstream of antigen binding.
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig),
It is a large, Y-shaped protein.
It is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
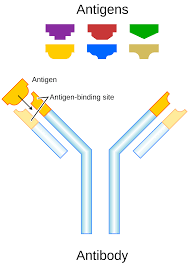
An antibody recognizes a unique molecule of a pathogen, called an antigen.
Each end of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision.
The binding mechanism of an antibody tags a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example.
Such binding can block a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion.
Antibodies bind to specific antigens, allowing the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens.
The antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in a wide variety of types, while the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant.
Antibodies occur in a few variants, which define the antibody’s class or isotype: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM.
The constant region of the antibody includes sites involved in interactions with other components of the immune system.
The class of antibody determines the function triggered by an antibody after binding to an antigen, in addition to some structural features.
Antibodies from different classes also differ in where they are released in the body and at what stage of an immune response.
Together with B and T cells, antibodies comprise the most important part of the adaptive immune system.
Antibodies occur in two forms: one that is attached to a B cell, and the other, a soluble form, that is unattached and found in extracellular fluids such as blood.
Initially, all antibodies are of the first form, attached to the surface of a B cell – these are then referred to as B-cell receptors (BCR).
When an antigen binds to a BCR, the B cell activates to proliferate and differentiate into either plasma cells, which secrete soluble antibodies with the same paratope, or memory B cells, which survive in the body to enable long-lasting immunity to the antigen.
Soluble antibodies are released into the blood, tissue fluids, and many secretions.
Antibody-mediated immunity is sometimes known as, or considered a part of, humoral immunity.
The soluble Y-shaped units can occur individually as monomers, or in complexes of two to five units.
Antibodies are glycoproteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily.
The terms antibody and immunoglobulin are often used interchangeably.
Antibodies are heavy (~150 kDa) proteins of about 10 nm in size, that are arranged in three globular regions that roughly form a Y shape.
An antibody unit consists of four polypeptide chains; two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains connected by disulfide bonds.
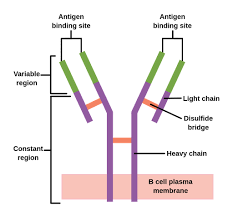
Immunoglobulins are composed of light chains and heavy chains.
The light chain (λ or κ) is a protein of ~220 amino acids, composed of a variable domain, VL (a segment of approximately 110 amino acids), and a constant domain, CL (also approximately 110 amino acids long).
Each chain is a series of domains: somewhat similar sequences of about 110 amino acids each.
Light chains consist of one variable domain VL and one constant domain CL, while heavy chains contain one variable domain VH and three to four constant domains CH1, CH2, etc.
Antibodies are partitioned into two antigen-binding fragments (Fab), containing one VL, VH, CL, and CH1 domain each, as well as the crystallisable fragment (Fc), forming the trunk of the Y shape.
In between these fragments is a hinge region of the heavy chains, whose flexibility allows antibodies to bind to pairs of epitopes at various distances.
They form complexes (dimers, trimers, etc.), to bind effector molecules more easily.
In electrophoresis test of blood proteins, antibodies mostly migrate to the last, gamma globulin fraction.
Most gamma-globulins are antibodies.
Gamma globulin and antibody are two terms were historically used as synonyms, as are their symbols Ig and γ.
The variable domains can also be referred to as the FV region.
The FV region is the subregion of Fab that binds to an antigen.
More specifically, each variable domain contains three hypervariable regions – the amino acids seen there vary the most from antibody to antibody.
When the protein folds, they give rise to three loops of β-strands, localized on the surface of the antibody referred to as the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), since their shape complements that of an antigen.
Three complementarity-determining regions from each of the heavy and light chains together form an antibody-binding site whose shape can be anything from a pocket to a larger surface, to a protrusion that sticks out into a groove in an antigen for binding.
The presence of two identical antibody-binding sites allows antibody molecules to bind strongly to multivalent antigens as well as to form antibody complexes and larger antigen-antibody complexes.
These cross-linkings plays a role in activating other parts of the immune system.
The structures of complementarity-determining regions are also called idiotypes, and the adaptive immune system is regulated by interactions between idiotypes.
Fragment crystallizable region(Fc region), is the trunk of the Y shape, and is composed of constant domains from the heavy chains.
The Fc region modulates immune cell activity: it is where effector molecules bind to, triggering various effects after the antibody Fab region binds to an antigen.
Effector cells-macrophages or natural killer cells, bind via their Fc receptors (FcR) to the Fc region of an antibody, while the complement system is activated by binding the C1q protein complex.
IgG or IgM can bind to C1q, but IgA cannot, therefore IgA does not activate the classical complement pathway.
The Fc region selectively distributes different antibody classes across the body: the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binds to the Fc region of IgG antibodies to transport it across the placenta, from the mother to the fetus.
Antibodies are glycoproteins with carbohydrates (glycans) added to conserved amino acid residues.
Each immunoglobulin domain has a similar structure, and is composed of between 7, for constant domains, and 9, for variable domains, β-strands, forming two beta sheets.
The sheets create a “sandwich” shape, the immunoglobulin fold, held together by a disulfide bond.
Some antibodies form complexes that bind to multiple antigen molecules.
Secreted antibodies can occur as a single Y-shaped unit, a monomer.
Antibodies also form complexes by binding to antigen: this is called an antigen-antibody complex or immune complex.
Small antigens can cross-link two antibodies, also leading to the formation of antibody dimers, trimers, tetramers, etc.
Multivalent antigens, cells with multiple epitopes, can form larger complexes with antibodies(clumping, or agglutination, of red blood cells with antibodies in the Coombs test to determine blood groups).
The membrane-bound form of an antibody may be called a surface immunoglobulin (sIg) or a membrane immunoglobulin (mIg).
It is part of the B cell receptor (BCR), which allows a B cell to detect when a specific antigen is present in the body and triggers B cell activation.
The BCR is composed of surface-bound IgD or IgM antibodies and associated Ig-α and Ig-β heterodimers, which are capable of signal transduction.
A typical human B cell will have 50,000 to 100,000 antibodies bound to its surface.
Upon antigen binding, the antibodies cluster in large patches, which can exceed 1 micrometer in diameter, isolating the BCRs from most other cell signaling receptors.
These antibody patches may improve the efficiency of the cellular immune response.
Antibodies can come in different varieties known as isotypes or classes.
There are five antibody classes known as IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM, which are further subdivided into subclasses such as IgA1, IgA2.
The prefix “Ig” stands for immunoglobulin, while the suffix denotes the type of heavy chain the antibody contains: the heavy chain types α (alpha), γ (gamma), δ (delta), ε (epsilon), μ (mu) give rise to IgA, IgG, IgD, IgE, IgM, respectively.
The distinctive features of each class are determined by the part of the heavy chain within the hinge and Fc region.
The antibody classes differ in their biological properties, functional locations and ability to deal with different antigens.
IgE antibodies are responsible for an allergic response consisting of histamine release from mast cells, often a sole contributor to asthma.
The antibody’s variable region binds to allergic antigen, for example house dust mite particles, while its Fc region in the ε heavy chains binds to Fc receptor ε on a mast cell, triggering its degranulation: the release of molecules stored in its granules.
IgA is found in mucosal areas, such as the gut, respiratory tract and urogenital tract, and prevents colonization by pathogens.
IgA is also present in saliva, tears, and breast milk.
IgD functions mainly as an antigen receptor on B cells that have not been exposed to antigens.
They activate basophils and mast cells to produce antimicrobial factors.
IgE binds to allergens and triggers histamine release from mast cells and basophils, and is involved in allergy.
IgE also protects against parasitic worms, though primarily related to allergies and asthma.
IgG4 In its four forms, provides the majority of antibody-based immunity against invading pathogens.
The only antibody capable of crossing the placenta to give passive immunity to the fetus.
IgM1 is expressed on the surface of B cells and in a secreted form with very high avidity.
IgM eliminates pathogens in the early stages of B cell-mediated humoral immunity before there is sufficient IgG.
The antibody isotype of a B cell changes during cell development and activation.
Immature B cells, which have never been exposed to an antigen, express only the IgM isotype in a cell surface bound form.
The B lymphocyte, in this form is known as a “naive B lymphocyte.”
The naive B lymphocyte expresses both surface IgM and IgD.
The co-expression of both of these immunoglobulin isotypes renders the B cell ready to respond to antigen.
B cell activation follows engagement of the cell-bound antibody molecule with an antigen, causing the cell to divide and differentiate into an antibody-producing cell called a plasma cell.
In its activated form, the plasma cell, B cell starts to produce antibody in a secreted form rather than a membrane-bound form.
Daughter cells of the activated B cells undergo isotype switching, that causes the production of antibodies to change from IgM or IgD to the other antibody isotypes, IgE, IgA, or IgG, that have defined roles in the immune system.
There are two types of immunoglobulin light chain, which are called lambda (λ) and kappa (κ).
There is no known functional difference between them, and both can occur with any of the five major types of heavy chains.
Each antibody contains two identical light chains: both κ or both λ.
Proportions of κ and λ types can be used to detect abnormal proliferation of B cell clones.
Antibodies and antigens interact by spatial complementarity lock and key function.
The molecular forces involved in the Fab-epitope interaction are weak and non-specific.
The binding between antibody and antigen is reversible, and the antibody’s affinity towards an antigen is relative rather than absolute.
Such relatively weak binding means it is possible for an antibody to cross-react with different antigens of different relative affinities.
The antibodies bind to pathogens by different formations such as:
opsonization, neutralisation, and agglutination.
A phagocyte (C) approaches the pathogen, and the Fc region (D) of the antibody binds to one of the Fc receptors (E) of the phagocyte.
Phagocytosis occurs as the pathogen is ingested.
The main categories of antibody action include the following:
Neutralisation, in which neutralizing antibodies block parts of the surface of a bacterial cell or virion to render its attack ineffective.
Agglutination, in which antibodies are glued together, putting foreign cells into clumps that are attractive targets for phagocytosis.
Precipitation, in which antibodies glue together serum-soluble antigens, forcing them to precipitate out of solution in clumps that are attractive targets for phagocytosis.
Complement activation-antibodies that are latched onto a foreign cell encourage complement to attack it with a membrane attack complex, which leads lysis of the foreign cell, encouragement of inflammation by chemotactically attracting inflammatory, and can signal immune cells to present antibody fragments to T cells, or downregulate other immune cells to avoid autoimmunity.
Activated B cells differentiate into either antibody-producing cells called plasma cells enaled to secrete soluble antibody or memory cells that survive in the body for years afterward in order to allow the immune system to remember an antigen and respond faster upon future exposures.
During prenatal and neonatal stages of life, antibodies are provided by passive immunization from the mother.
Early endogenous antibody production varies for different kinds of antibodies, and usually appear within the first years of life.
Sntibodies exist freely in the bloodstream, they are said to be part of the humoral immune system.
Circulating antibodies are produced by clonal B cells that specifically respond to only one antigen.
Antibodies contribute to immunity in three ways: They prevent pathogens from entering or damaging cells by binding to them; they stimulate removal of pathogens by macrophages and other cells by coating the pathogen; and they trigger destruction of pathogens by stimulating other immune responses such as the complement pathway.
Antibodies will also trigger vasoactive amine degranulation to contribute to immunity against certain types of antigens (helminths, allergens).
The secreted IgM has five Ig units.
Each Ig unit has two epitope binding Fab regions, so IgM is capable of binding up to 10 epitopes.
Antibodies that bind to surface antigens attract the first component of the complement cascade with their Fc region and initiate activation of the classical complement system.
This results in the killing of bacteria by binding of the antibody and complement molecules for ingestion by phagocytes in a process called opsonization.
Phagocytes are attracted by certain complement molecules generated in the complement cascade.
Some complement system components form a membrane attack complex to assist antibodies to kill the bacterium directly.
For pathogens that replicate outside cells, antibodies bind to pathogens to link them together, causing them to agglutinate.
An antibody has at least two paratopes, it can bind more than one antigen by binding identical epitopes carried on the surfaces of these antigens.
By coating the pathogen, antibodies stimulate effector functions against the pathogen in cells that recognize their Fc region.
Cells that recognize coated pathogens have Fc receptors, which interact with the Fc region of IgA, IgG, and IgE antibodies.
The engagement of a particular antibody with the Fc receptor on a particular cell triggers an effector function of that cell; phagocytes will phagocytose, mast cells and neutrophils will degranulate, natural killer cells will release cytokines and cytotoxic molecules; that will ultimately result in destruction of the invading microbe.
The activation of natural killer cells by antibodies initiates a cytotoxic mechanism known as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
The antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) explains the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies used in biological therapies against cancer.
The Fc receptors are isotype-specific, as they invoking only the appropriate immune mechanisms for distinct pathogens.
Humans produce natural antibodies that are present in serum before viral infection, and they are defined as antibodies that are produced without any previous infection, vaccination, other foreign antigen exposure or passive immunization.
These natural antibodies can activate the classical complement pathway leading to lysis of enveloped virus particles long before the adaptive immune response is activated.
Many natural antibodies are formed against the disaccharide galactose α(1,3)-galactose (α-Gal).
The disaccharide galactose α(1,3)-galactose (α-Gal) is found as a terminal sugar on glycosylated cell surface proteins, and generated in response to production of this sugar by bacteria contained in the human gut.
Rejection of xenotransplantated organs is thought to be, in part, due to natural antibodies circulating in the serum of the recipient binding to α-Gal antigens expressed on the donor tissue.
Virtually all microbes can trigger an antibody response.
To be successful to recognize and eradication of many different types of microbes requires diversity among antibodies; their amino acid composition varies allowing them to interact with many different antigens.
It has been estimated that humans generate about 10 billion different antibodies, each capable of binding a distinct epitope of an antigen.
The chromosomal region that encodes an antibody is large and contains several distinct gene loci for each domain of the antibody.
The chromosome region containing heavy chain genes is found on chromosome 14.
The loci containing lambda and kappa light chain genes are found on chromosomes 22 and 2 in humans.
One of these domains is called the variable domain, which is present in each heavy and light chain of every antibody.
These domains differ in different antibodies generated from distinct B cells.
Differences between the variable domains are located on three hypervariable regions (HV-1, HV-2 and HV-3) or complementarity-determining regions (CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3).
Heavy chain locus contains about 65 different variable domain genes that all differ in their CDRs, generatina large cavalry of antibodies with a high degree of variability.
Combining these genes with an array of genes for other domains of the antibody generates a large number of antibodies with a high degree of variability.
Somatic recombination of immunoglobulins, is known as V(D)J recombination, involves the generation of a unique immunoglobulin variable region.
The variable region of each immunoglobulin heavy or light chain is encoded in gene segments (subgenes).
These segments are called variable (V), diversity (D) and joining (J) segments.
V, D and J segments are found in Ig heavy chains, but only V and J segments are found in Ig light chains.
In the bone marrow, developing B cells will assemble an immunoglobulin variable region by randomly selecting and combining one V, one D and one J gene segment (or one V and one J segment in the light chain).
Multiple copies of each type of gene segment exist, and different combinations of gene segments generate each immunoglobulin variable region, generating a huge number of antibodies, wuith different antigen specificities.
After a B cell produces a functional immunoglobulin gene during V(D)J recombination, it cannot express any other variable region, and each B cell can produce antibodies containing only one kind of variable chain.
Following antigen activation, B cells begin to proliferate rapidly.
The genes encoding the variable domains of the heavy and light chains undergo a high rate of point mutation called somatic hypermutation (SHM).
Such somatic hypermutation results in approximately one nucleotide change per variable gene, per cell division, so that daughter B cells will acquire slight amino acid differences in the variable domains of their antibody chains.
This process increases the diversity of the antibody pool and impacts the antibody’s antigen-binding affinity.
Some point mutations will result in the production of antibodies that have a weaker interaction/low affinity with their antigen than the original antibody, and some mutations will generate antibodies with a stronger affinity.
B cells expressing antibodies with a higher affinity for the antigen will outcompete those with weaker affinities, allowing the average affinity of antibodies to increase over time.
The generation of antibodies with increased binding affinities is called affinity maturation.
Affinity maturation occurs in mature B cells after V(D)J recombination, and is dependent on help from helper T cells.
Isotype/class switching is a biological process occurring after activation of the B cell, which allows the cell to produce different classes of antibody (IgA, IgE, or IgG).
The different classes of antibody, are defined by the constant (C) regions of the immunoglobulin heavy chain.
Initially, naive B cells express only cell-surface IgM and IgD with identical antigen binding regions.
Each isotype is adapted for a distinct function; therefore, after activation, an antibody with an IgG, IgA, or IgE effector function might be required to effectively eliminate an antigen.
Class switching allows different daughter cells from the same activated B cell to produce antibodies of different isotypes.
Only the constant region of the antibody heavy chain changes during class switching; the variable regions, and therefore antigen specificity, remain unchanged.
Thus the progeny of a single B cell can produce antibodies, with the ability to produce the effector function appropriate for each antigenic challenge.
Class switching is triggered by cytokines present in the B cell environment.
An antibody is called monospecific if it has specificity for the same antigen or epitope, or bispecific if they have affinity for two different antigens or two different epitopes on the same antigen.
Antibodies can be called polyvalent/ unspecific if they have affinity for various antigens or microorganisms.
Intravenous immunoglobulin, if not otherwise noted, consists of a variety of different IgG.
In contrast, monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single B cell.
Antibody bispecificity allows for the binding specificities of two different antigens.
Pharmaceuticals are able to produce highly functional bispecific, and even multispecific, antibodies.
Levels of individual classes of immunoglobulins are measured to characterize the antibody profile of patient.
Elevations in different classes of immunoglobulins are useful in determining the cause of liver damage in patients for whom the diagnosis is unclear.
For example, elevated IgA indicates alcoholic cirrhosis, elevated IgM indicates viral hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis, while IgG is elevated in viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Autoimmune disorders can often be traced to antibodies that bind the body’s own epitopes; many can be detected through blood tests.
Antibodies directed against red blood cell surface antigens in immune mediated hemolytic anemia are detected with the Coombs test.
The Coombs test is also used for antibody screening in blood transfusion preparation and also for antibody screening in antenatal women.
Immunodiagnostic methods to detect complex antigen-antibody are used to diagnose infectious diseases, for example ELISA, immunofluorescence, Western blot, immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, and magnetic immunoassay.
Antibodies raised against human chorionic gonadotropin are used in over the counter pregnancy tests.
New dioxaboroadioactive fluoride (18F) labeling of antibodies allows for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of cancer.
Targeted monoclonal antibody therapy treats diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, and many forms of cancer including non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer and breast cancer.
Some immune deficiencies, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia and hypogammaglobulinemia, result in partial or complete lack of antibodies.
Rh factor, also known as Rh D antigen, is an antigen found on red blood cells.
Rh-positive (Rh+) individuals have this antigen on their red blood cells and individuals that are Rh-negative (Rh–) do not.
During normal childbirth, delivery trauma or complications during pregnancy, blood from a fetus can enter the mother’s system.
In there is a case of an Rh-incompatible mother and child, consequential blood mixing may sensitize an Rh- mother to the Rh antigen on the blood cells of the Rh+ child, putting the remainder of the pregnancy, and any subsequent pregnancies, at risk for hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Anti-RhD antibodies are administered as part of a prenatal treatment regimen to prevent sensitization that may occur when a Rh-negative mother has a Rh-positive fetus.
Treatment of a mother with Anti-RhD antibodies prior to and immediately after trauma and delivery destroys Rh antigen in the mother’s system from the fetus.
The antigen can stimulate maternal B cells to remember Rh antigen by generating memory B cells, and humoral immune system will not make anti-Rh antibodies, and will not attack the Rh antigens of the current or subsequent babies.
Rho(D) Immune Globulin treatment prevents sensitization that can lead to Rh disease.
Most antibodies are produced by hybridoma cell lines through immortalization of antibody-producing cells by chemically induced fusion with myeloma cells.
Such events include complement, fixation, and antibody dependent cellular toxicity.
The ability of the immune system to generate a glycoprotein capable of recognizing foreign proteins, while ignoring self antigens, is not fully understood.
Monoclonal antibodies, have a defined specificity, binding to specific epitropes on a specific antigen, and is derived from a single, immortalized B cell clone.
Bifunctional antibodies are anybody molecules in which one arm targets a tumor antigen, and another arm targets a T cell surface molecule such as CD3.
