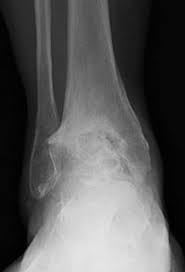
 Osteoarthritis of the ankle occurs when the cartilage between the bones erode.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle occurs when the cartilage between the bones erode.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle affects around 1% of the population.
In a normal ankle, cartilage covers the bone surfaces that meet, serving as protective padding.
In osteoarthritis of the ankle, the cartilage gradually wears away, and as a result, the bones rub against each other, leading to the formation of painful bone spurs.
The main cause of ankle osteoarthritis is trauma, usually from a rotational injury resulting in ligament sprains and bone fractures.
These injuries tends to occur in younger people.
It can cause stiffness, swelling, and pain in the joint, which makes walking difficult.
Symptoms worsen over time and the stiffness and pain is worse in the morning.
Swelling on one side or all around the joint can occur.
There is reduced range of motion,
tenderness upon touching or squeezing the joint and difficulty walking
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, gait analysis, X-rays, and blood tests.
Following diagnosis, doctors may recommend weight loss, exercise, and a change in activities to reduce or manage symptoms.
Treatment includes non-drug measures, medications, and surgery.
Management includes:
weight loss to decrease pressure on the ankle
topical creams with ingredients that reduce pain or inflammation, such as capsaicin, cannabidiol, camphor, and menthol
physical therapy
avoiding the activities that produce the most pain
use of shoe inserts, a cane, or a brace
Drug treatments:
Acetaminophen, NSAIDs.
Injections involve glucocorticoids, provide short-term pain relief.
When treatments do not manage pain or improve mobility:
Arthrodesis: This fuses the bones of the ankle.
Arthroscopic surgery to remove bone spurs and loose cartilage.
Total ankle replacement.
Complete recovery from surgery may take 4–9 months, but most individuals can resume their regular activities in 3–4 months.
Exercises
Experts recommend gentle exercises that do not put stress on the ankle, such as:
walking
swimming
cycling
Avoiding certain sports, such as kickboxing and soccer, and limiting high impact activities, such as running or tennis.
Additionally, physical therapists can provide an individualized exercise program to increase the ankle’s range of motion, flexibility, and strength: Plantar flexion, Dorsiflexion, Ankle circles.
Diagnosis
Physical examination to demonstrate swelling and tenderness.
History of pain, onset and characteristics.
Gait analysis also includes: measurement of stride
assessment of bone lineup during walking
strength test of ankle and foot.
X-ray imagine can reveal narrowing of joint space between ankle bones, as well as spurs and other changes, such as fractures or breaks.
It is not possible to cure or reverse osteoarthritis, but treatment can reduce pain and enable a person to perform their everyday activities.
In most case surgery reduces pain and enables people to function.
