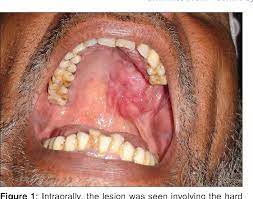
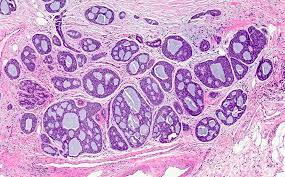
 Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different most often sites, but occurs mainly in the salivary glands.
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different most often sites, but occurs mainly in the salivary glands.
It can also be found in many anatomic sites, including the breast, lacrimal gland, lung, brain, Bartholin gland, trachea, and the paranasal sinuses.
ACC is the third-most common malignant salivary gland tumor overall.
It follows mucoepidermoid carcinoma and polymorphous adenocarcinoma.
It represents 28% of malignant submandibular gland tumors, making ACC the most common malignant salivary gland tumor in this region.
73% of cases are identified in salivary glands and is found in 2% of cases in lacrimal glands.
Lacrimal gland ACC occurs in about 25 patients per year in the US and is the second most common type of cancer in the lacrimal gland, after lymphoma.
Lacrimal gland ACC has a worse prognosis than ACC of the salivary gland.
Patients may survive for years with metastases because this tumor is generally well-differentiated and slow growing.
In a 1999 study of a cohort of 160 ACC patients, disease-specific survival was 89% at 5 years, but only 40% at 15 years, a reflection that deaths are from late-occurring metastatic disease.
The oncogenic transcription factor gene MYB is the key genomic event in ACC.
MYB gene is seen in the vast majority of cases.
MYB drives proliferation of ACC cells and regulates genes involved in cell cycle control, DNA replication and repair, and RNA processing.
Treatments:
Primary treatment for this cancer, regardless of body site, is surgical removal.
In the head and neck region ACCs have a tendency to show a perineural discontinuous growth, and different collection of the tumor cells can exist without a connection to the original tumor.
MRI-imaging should be analyzed following nerve tracts up to the brainstem.
Adjuvant or palliative radiotherapy is commonly given following surgery.
For advanced major and minor salivary gland tumors that are inoperable, or recurrent, or have gross residual disease after surgery, fast neutron therapy is the most effective form of treatment.
Chemotherapy is used for metastatic disease, but data on the positive effects of chemotherapy are limited.
