 Characterized by abnormally increased growth and impaired maturation of blood forming cells.
Characterized by abnormally increased growth and impaired maturation of blood forming cells.
Develops when the DNA sequence on genes of a blood forming cell is altered by gains or losses of DNA material in one or more chromosomes.
In 2006 approximately 35,000 new cases in the U.S. with 30% of the cases being Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
The incidence increases with age, especially for AML and CLL.
ALL is the most common form of childhood leukemia.
Exposure to common viral infections in early childhood is associated with a reduced risk of leukemia.
In most cases the cause of DNA sequence alterations is unknown.
Exposure to chemotherapy and radiation may increase the risk
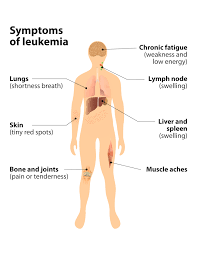
Symptoms include pallor, weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath, headache, increased susceptibility to infections, skin lesions, fever, chills, recurrent urinary tract infections, recurrent peri-anal infections, gum bleeding epistaxis, easy bruising and the development of petechiae, bone pain abdominal tenderness, lymph node enlargement and gum swelling.
Symptoms of acute leukemia progress rapidly over days, while chronic leukemia may not manifest for months.
Diagnosis of the type of leukemia present relates to the identification of an abnormal number or appearance of cells in the peripheral blood.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is made by examination of the bone marrow.
Leukocytosis-refers to an increase in the number of blood leukocytes.
