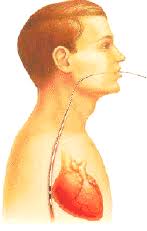
 Transcsophageal atrial stimulation (TAS) and recording is used in a wide spectrum of clinical settings: induction and termination of reentrant supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial flutter, the differential diagnosis between atrial flutter, atrioventricular (AV) nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), and orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia (ORT) using an accessory pathway, and the risk evaluation of patients with the Wolff-Purkinson-White (WPW) syndrome.
Transcsophageal atrial stimulation (TAS) and recording is used in a wide spectrum of clinical settings: induction and termination of reentrant supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial flutter, the differential diagnosis between atrial flutter, atrioventricular (AV) nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), and orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia (ORT) using an accessory pathway, and the risk evaluation of patients with the Wolff-Purkinson-White (WPW) syndrome.
Other applications include the evaluation of the pro-phylactic effect of antiarrhytmic drug treatment in putients with SVT, and the assessment of the sinus node and AV node function in patients with symptoms consistent with bradyarrhythmias.
It is noninvasive, requires no fluoroscopy, and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
This makes it feasible for cardiologists working in smaller hospitals.
