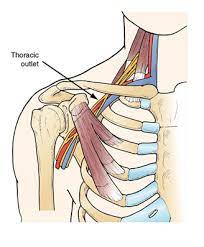
 The presence of a cervical rib can compress the subclavian artery and the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus involving C8 and T1.
The presence of a cervical rib can compress the subclavian artery and the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus involving C8 and T1.
The syndrome can occur in patients with hypertrophy of the anterior scalene muscles and in hyper abduction injuries of the arm.
It may be caused by a number of abnormalities, including: degenerative or bony disorders, trauma to the cervical spine, fibromuscular bands, vascular abnormalities, and spasm of the anterior scalene muscle.
Symptoms are due to compression of the brachial plexus and subclavian vasculature, and consist of complaints ranging from diffuse arm pain to a sensation of arm fatigue.
Associated with thenar and hypothenar atrophy, atrophy of the interosseous muscles and sensory abnormalities of the median forearm and hand.
When the head is rotated toward the opposite side of the compression the radial arterial pulse disappears as the subclavian artery is compressed (Adson’s sign).
Treatment is an anterior scalenectomy and physical therapy.
