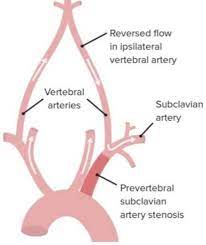
Retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion.
Occurs when the subclavian artery is occluded proximal to the vertebral artery.
Neurological symptoms with arm exercise in the ipsilateral arm is uncommon.
Most patients wit significant arterial occlusion in the proximal subclavian artery are asymptomatic.
Subclavian steal syndrome actually refers to the presence of neurological symptoms.
Neurological symptoms with arm exercise relates to brain ischemia that occurs during or immediately following ipsilateral arm exercise.
Decreased blood pressure occurs in the ipsilateral arm.
The left subclavian artery involved three times more commonly than the right subclavian artery.
Prevalence of the process is unknown.
Most common cause is related to occlusive atherosclerosis lesions.
Risks related to atherosclerosis with age, male gender and family history being nonmodifiable factors.
Modifiable risk factors include smoking abuse, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension an hyperhomocysteinemia.
May be associated with pain on swallowing, dysphasia lusoria, caused by compression of the esophagus from the subclavian artery
