 A skin infection is an infection of the skin that can also affect the associated soft tissues such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes.
A skin infection is an infection of the skin that can also affect the associated soft tissues such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes.
Skin infection comprises a category of infections termed skin and skin structure infections,or skin and soft tissue infections and acute bacterial skin infections.
Skin infection is distinguished from dermatitis,an inflammation of the skin.
Bacterial skin infections include:
Cellulitis, a diffuse inflammation of connective tissue with severe inflammation of dermal and subcutaneous layers of the skin.
Cellulitis is classified based into purulent and non-purulent cellulitis.
Purulent cellulitis is often caused by Staphylococcus aureus, including both methicillin-sensitive (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA).
Non-purulent cellulitis is most often associated with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, such as Streptococcus pyogenes
In rare cases a skin infection can progress into necrotizing fasciitis, a serious and potentially fatal infection.
Erysipelas is a bacterial infection which primarily affects superficial dermis, and often involves superficial lymphatics.
Unlike cellulitis, it does not affect deeper layers of the skin.
Erysipelas is primarily caused by the Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, with Streptococcus pyogenes being the most common pathogen.
Folliculitis, a skin condition in which hair follicle, located in the dermal layer of the skin, becomes infected and inflamed.
It is predominantly caused by bacterial infections, especially Staphylococcus aureus, leading to superficial bacterial folliculitis.
Other causes of folliculitis include: fungi (most commonly Malassezia species), viruses (such as herpes simplex virus), and mites (Demodex species).
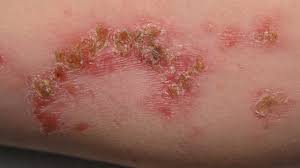
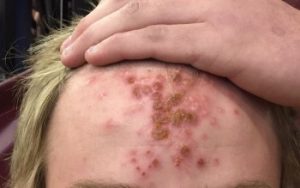
Impetigo, a highly contagious acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection common among pre-school children, primarily associated with the pathogens S. aureus and S. pyogenes.
Impetigo. has a characteristic appearance with yellow (honey-colored), crusted lesions occurring around mouth, nose, and chin.
Estimated that at any given time, it affects 140 million people globally.
Impetigo can be classified into bullous and nonbullous forms.
Nonbullous impetigo is the most common form, representing approximately 70% of diagnosed cases.
The remaining 30% of cases represent bullous form, which is primarily caused by S. aureus.
Rarely, bullous impetigo can spread and lead to Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), a potentially life-threatening infection.
Fungal skin infections may be either a superficial or deep infection of the skin, hair, and/or nails.
Mycetoma are a broad group of fungal infections that characteristically originate in the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the foot.
Mycetoma infections can extend to deeper tissues like bones and joints causing osteomyelitis.
Mycetoma affect more than one billion people globally.
Some common fungal skin infections include:
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a superficial fungal infection of the skin caused by several different species of fungi:
genera which cause skin infections in humans include Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum.
Dermatophytosis is more prevalent in areas with high humidity and environmental temperature.
It is estimated that approximately 20-25% of world population are affected by superficial fungal infections, with dermatophytosis predominating.
Oral candidiasis, also commonly referred to as oral thrush, is a fungal infection caused mainly by Candida albicans, which affects mucosal membranes of the oral cavity and the tongue.
C. albicans accounts for approximately 95% of oral thrush cases.
The fungus is part of the normal oral flora and only causes an infection when host immune and microbiota barriers are impaired, providing C. albicans with an opportunity to overgrow.
It is estimated that oral candidiasis affects approximately 2 million people every year worldwide.
Onychomycosis, a fungal infection which predominantly affects toenails.
Two most common causative agents of onychomycosis are Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton rubrum.
Onychomycosis signs and symptoms include nail discoloration and thickening, nail separation from nail bed, and nail brittleness.[
Estimated prevalence of onychomycosis in North America is between 8.7% to 13.8%.
Parasitic infestations of the skin can be caused by several phyla of organisms.
Virus-related cutaneous conditions caused obligate intracellular agents that are derive from both DNA and RNA viruses.
Viral skin infections include:
Warts, benign proliferative skin lesions that are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).
Warts vary in shape, size, appearance, and location on the body.
Plantar warts (verrucae plantaris), occur on the soles of the feet and appear as thick calluses.
Other types of warts include genital warts, flat warts, mosaic warts, and periungual warts.
Common treatment options include salicylic acid and cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen.
Chickenpox, is a highly contagious skin disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
Chickenpox is characterized by pruritic blister-like rash which may cover entire body, affecting all age groups.
Rates of chickenpox are higher in countries which lack adequate immunization programs.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), is a common, often self-limiting viral illness which typically affects infants and children, however, it may also occur in adults.
It is characterized by low grade fever and maculopapular rash on palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and around mouth.
It is caused by the human enteroviruses and coxsackieviruses, a positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses.
