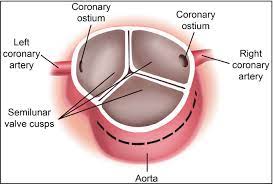
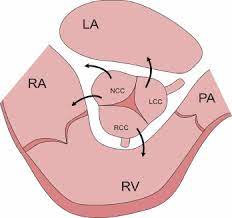
An aortic sinus, also known as a sinus of Valsalva, is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve.
These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic valve.
There are generally three aortic sinuses, one anterior and two posterior sinuses.
The aortic sinuses give rise to coronary arteries:
The left aortic or left posterior aortic sinus gives rise to the left coronary artery.
The right aortic or anterior aortic sinus gives rise to the right coronary artery.
The posterior aortic or right posterior aortic sinus usually gives rise to no vessels, and is often known as the non-coronary sinus.
Aortic sinuses are typically more prominent than the pulmonary sinuses.
If the coronary arteries arise from the wrong aortic sinuses, this can put the heart’s ventricles at risk of ischaemia.
