 Also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare disorder of unknown etiology that is characterized by abundant histiocytes in the lymph nodes throughout the body.
Also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare disorder of unknown etiology that is characterized by abundant histiocytes in the lymph nodes throughout the body.
A histiocytic disorder of unknown origin.
A non-malignant process characterized by massive lymphadenopathy.
An inflammatory disease process
Prevalence is approximately one per 200,000 people.
Lymphadenopathy of the neck is the most common place of histiocyte accumulation.
Typically associated with painless, often bilateral, cervical lymphadenopathy which may be accompanied by fever, leukocytosis, elevated sedimentation rate, and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia.
Extranodal disease present in approximately one third of cases.
The most common sites of accumulation outside of the lymph nodes are skin, upper respiratory tract, and the sinuses.
Extra nodal disease may occur in the upper and lower respiratory tracts, skin, bone, joints, lungs, thyroid, eyes, eyelids, thyroid, kidney, testes, sinus, heart, liver, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, pancreas, jejunum, CNS, and meningitis.
The skin is the most common extranodal site of involvement of R-D disease.
Extra oral disease is more common in Asians.
The symptoms of this disease vary with the site of the lesions.
Usually a non-progressive and self-limited process.
Can manifest as an autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
May be associated with hemoptysis.
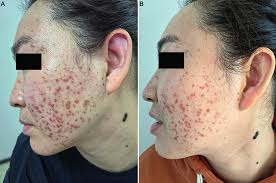
Skin lesions maybe single, multiple, and maybe papular, nodular, plaque like or combination of these.
Skin lesions may also be pustular, psoriasis like, acnelike and vary in size from less than 1 to 30 cm.
Cutaneous disease may be asymptomatic and chronic and does not require treatment as it is a benign process and may spontaneously regress after months or years.
Cutaneous variant may have recurrences over the years and may have complications in about 5 to 11% of cases.
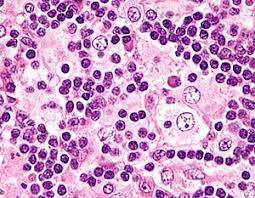
Histopathology and histochemical testing provide diagnosis with emperiopoiesis, involving engulfment of intact lymphocytes and plasma cells by histiocytes.
Immunohistology cells are CD68 and S100 positive.
In patients that require therapy or that have rapid progression treatment options include surgical excision, radiotherapy, cryotherapy, thalidomide, isoretinoin acid, intralesional steroids and rituximab.
