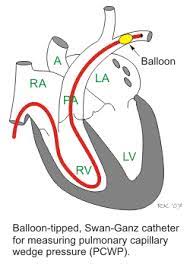
 The pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP), also called pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP), and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP).
The pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP), also called pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP), and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP).
PWP is the pressure measured by wedging a pulmonary catheter with an inflated balloon into a small pulmonary arterial branch.
PWP estimates the left atrial pressure.
Pulmonary venous wedge pressure correlated with pulmonary artery pressures in studies.
Distinctions between pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary venous pressure and left atrial pressure can be made.
Pressure range
(in mmHg)
Central venous pressure 3–8
Right ventricular pressure systolic 15–30
diastolic 3–8
Pulmonary artery pressure systolic 15–30
diastolic 4–12
Pulmonary vein/
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
2–15
Left ventricular pressure systolic 100–140
diastolic 3–12
Because of the large compliance of pulmonary circulation, it provides an indirect measure of the left atrial pressure.
Acute pulmonary edema; this is likely to be present at a PWP of >20mmHg.
PWP can be used to diagnose severity of left ventricular failure and mitral stenosis, given that elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure strongly suggests failure of left ventricular output.
