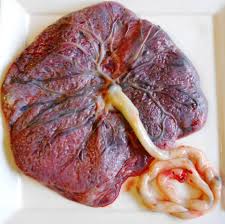
 Supplies nutrients to the embryo and also removes wastes via the interaction with the maternal circulation.
Supplies nutrients to the embryo and also removes wastes via the interaction with the maternal circulation.
Chorion is the fetal contribution to the placenta and includes somatic extraembryonic mesoderm, cytotrophoblast, and syncytiotrophoblast.
The syncytiotrophoblast invades the maternal tissue and blood vessels forming tissue lacunae and fills with maternal blood.
Syncytiotrophoblasts produce glycoprotein, hormones, growth hormones, steroids, neuropeptides, metallopeptidases, and senescent associated secretary proteins.
The placenta is intensely secretory in late gestation.
The villi which are exchange units form in stages : primary, secondary and tertiary.
The primary villi consist of a cytotrophoblast core with a syncytiotrophoblast covering, the secondary villi form when the core of the primary villi is invaded by extraembryonic mesoderm and the tertiary villi are formed when the core of the secondary villi develop vasculature.
The maternal side of the placenta develops as the cytotrophoblast grows through the villi and the cytotrophoblast connects with the villi.
Protects the fetus against unwarranted chemical exposure but not an effective barrier of environmental pollutants.
Many metals such as mercury readily cross the placental barrier.
The extraembryonic mesoderm on the embryonic side is connected at its base to the chorionic plate, and extension of the villi from the chorionic plate to the cytotrophoblast shell anchors the placenta to the uterus.
The decidua is the epithelial lining of the endometrium and it participates in the anchoring of the placenta.
