 PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum (PROS) is an umbrella term for rare syndromes characterized by malformations and tissue overgrowth caused by somatic mutations in PIK3CA gene.
PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum (PROS) is an umbrella term for rare syndromes characterized by malformations and tissue overgrowth caused by somatic mutations in PIK3CA gene.
PROS is usually caused by somatic mutations in the PIK3CA gene.
Rarely, PROS is caused by a de novo germline mutation, which is present in all cells of the body.
These somatic mutations are typically only present in some cells or some areas of the body; mosaicism, and are not known to be inherited.
In PROS malformations are seen in several different tissues such as skin, vasculature, bones, fat and brain tissue depending on the specific disease.
Signs and symptoms of PROS depend on the specific disorder present.
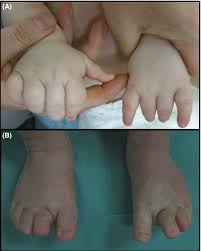
Findings can include having a larger-than-normal brain (megalencephaly), low muscle tone (hypotonia), seizures, intellectual disability, changes in the blood vessels (vascular system), and overgrowth of one area of the body (focal overgrowth) or of multiple areas of the body (segmental overgrowth), with normal growth elsewhere.
Diseases include:
Fibro-adipose vascular anomaly
Hemihyperplasia–multiple lipomatosis syndrome
CLOVES syndrome
Macrodactyly
Facial infiltrating lipomatosis
Macrocephaly-capillary malformation
Dysplastic megalencephaly
Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
PIK3CA gene codes for p110α protein.
p110a protein is a catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, a major regulator of several important cellular functions such as cell proliferation, growth and apoptosis.
Mutations in PIK3CA cause over-activity of PI3K which leads to altered growth of cells and tissues which is thought to be important for overgrowth and malformations in PROS.
PROS disease variations are likely explained by acquisition of the mutation in different time points and different cell types during embryonic development
Diagnosis of a PROS disorder can be confirmed with genetic testing of the PIK3CA gene.
Treatment for a PROS disorder may involve surgical interventions, special education, and speech and physical therapies.
Treatment depends on the specific disease.
Curative treatment does not exist.
Overgrowth and malformations of solid tissues can be treated with surgery.
Sclerotherapy is available to treat vascular malformations.
In CLOVES syndrome medical therapy using PIK3CA inhibitors reported to be effective to relieve pain and diminish the malformations.
