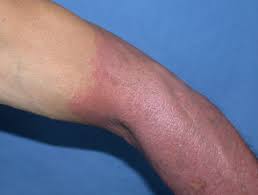
 Photosensitivity refers to abnormal reactions of the skin upon receiving photons, especially visible light.
Photosensitivity refers to abnormal reactions of the skin upon receiving photons, especially visible light.
There are two types: photoallergy and phototoxicity.
People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn.
Exposure to UV rays can lead to skin damage and skin cancer.
People who are photosensitive may develop skin rashes or burns, even after only limited exposure to the sun.
Medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight include: tetracycline antibiotics, amiodarone, sulfonamides , chemotherapy, diuretics and St. John’s Wort.
Phototoxic reactions are caused when a new chemical in the body interacts with UV rays from the sun.
Phototoxic reactions are non-immunological response to sunlight interacting with certain drugs and chemicals in the skin which resembles an exaggerated sunburn.
Common drugs that may cause a phototoxic reaction include amiodarone, dacarbazine, fluoroquinolones, 5-fluorouracil, furosemide, nalidixic acid, phenothiazines, psoralens, retinoids, sulfonamides, sulfonylureas, tetracyclines, thiazides, and vinblastine.
Medical conditions associated with light sensitivity: systemic lupus erythematosus, some types of porphyria are aggravated by sunlight, xeroderma pigmentosum.
In hepatogenous photosensitization, the photosensitzing substance is phylloerythrin, a normal end-product of chlorophyll metabolism.
It accumulates in the body because of liver damage, reacts with UV light on the skin, and leads to free radical formation.
Free radicals damage the skin, leading to ulceration, necrosis, and sloughing.
Non-pigmented skin is most commonly affected.
Photoallergic reactions can develop as a side effect of some medications, and can also arise from chemicals found in beauty products and sunscreen.
Photoallergic reactions: Uncommon immunological response to sunlight interacting with certain drugs and chemicals in the skin.
When in excited state by UVR, these drugs and chemicals form free radicals that react to form functional antigens and induce a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
These drugs include 6-methylcoumarin, aminobenzoic acid and esters, chlorpromazine, promethazine, diclofenac, sulfonamides, and sulfonylureas.
Unlike phototoxic reactions which resemble exaggerated sunburns, photoallergic reactions can cause intense itching and can lead to thickening of the skin.
These types of reactions to the sun tend to take a few days for a rash to develop after sun exposure.
Symptoms of photosensitivity vary from mild to severe.
The most common symptom is an exaggerated skin rash or sunburn: blistering may develop with weeping and peeling.
Medical conditions that can cause photosensitivity:
Lupus erythematous
Polymorphous light eruption
Actinic prurigo: People with this condition may develop red bumps after sun exposure, which can turn into scaly patches.
TREATMENT:
Over-the-counter pain medications can relieve pain and corticosteroid cream may be prescribed to decrease inflammation.
Prevention:
Limiting the amount of time in the sun.
People who are photosensitive should always use sunscreen when outside.
Chemicals and medications that cause photosensitivity and should be avoided.
Covering and protecting the skin: wearing hats, sunglasses, and shirts with long sleeves when outside.
