 A smooth membrane that covers the abdominal walls and viscera of the abdomen and pelvis.
A smooth membrane that covers the abdominal walls and viscera of the abdomen and pelvis.
The peritoneum it is an extensive serous membrane that covers the abdominal pelvic organs and abdominal wall and functions to include intraperitoneal homeostasis.
It approximates body surface area in size.
Is a continuous sheet of sinlge layered mesothelial cells supported by connective tissue and forms the visceral and parietal peritoneum.
The space between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is called the peritoneal cavity.
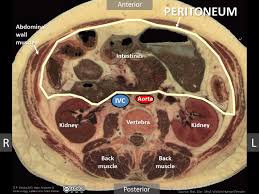
Itis composed of two layers: the visceral peritoneum, which covers abdominal organs and accounts for 80% of the total surface area, and the parietal peritoneum, which lines the under surface of the diaphragm and the interior service of the interior abdominal wall
The parietal peritoneum lines the entire abdominal cavity.
The peritoneum histologically consists of a single layer of mesothelial cells resting on a submesothelial interstitial tissue, a gel like matrix containing fibroblasts, adipocytes, collagen fibers, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and capillaries.
The endothelium of the peritoneum‘s capillaries functions is the filter that regulates peritoneal transport.
The peritoneum therefore provides a suitable remembering for the performance of dialysis.
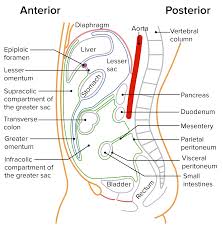
Posteriorly the peritoneum comes together to form a double membrane known as the mesentery.
Abdominal organs are suspended from the mesentery and they separate into sheets which surrounf the organs and is the visceral peritoneum.
Mesentery that extends beyond organs and forms a four layered structure in 2 areas is the omentum, the lesser and greater omenta.
Peritonitis refers to inflammation of the peritoneum.
The peritoneum is lubricated by a small amount of fluid formed from the ultrafiltration of the plasma.
