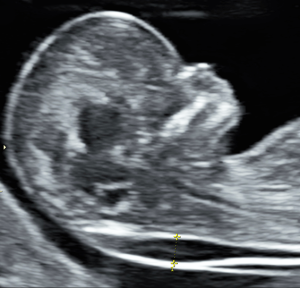
 Evaluation of fetus by sonogram by measuring nuchal translucency in a midsagittal plane in the first trimester.
Evaluation of fetus by sonogram by measuring nuchal translucency in a midsagittal plane in the first trimester.
A thickness of more than 5 to 6 mm is considered abnormal during the first trimester.
The nuchal fold refers to a measurement taken during prenatal ultrasound screening, typically between 11-14 weeks of pregnancy. Here’s a brief overview:
The nuchal fold is a fluid-filled space at the back of a developing fetus’s neck.
Measuring the nuchal fold thickness is part of screening for certain chromosomal abnormalities, particularly Down syndrome (Trisomy 21).
The measurement is taken via ultrasound, looking at the fluid-filled space between the back of the fetal neck and the overlying skin.
Generally, a measurement less than 3mm is considered normal, though this can vary based on the fetus’s gestational age.
A thicker nuchal fold may indicate a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities or other congenital conditions.
An increased measurement doesn’t necessarily mean there’s a problem – it’s a screening tool, not a diagnostic test.
If an increased thickness is found, doctors may recommend additional tests like cell-free DNA screening or diagnostic tests such as amniocentesis.
