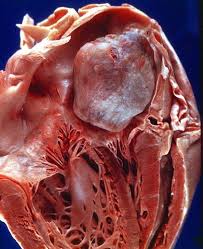
 Accounts for one third of primary cardiac tumors.
Accounts for one third of primary cardiac tumors.
The incidence is about 0.5 per million population per year.
Cardiac myxomas make up nearly half of all primary cardiac tumors.
Metastases or invasion of other tumors to the heart are about 20 times more common than primary cardiac tumors.
75% involve the left atrium and 15% arise fro the right atrium.
Occur most often in the third through sixth decades of life and affect women more than men.
Rarely associated with the ((Carney complex)), an autosomal dominant condition, with cardiac and cutaneous myxomas Lentinginosis, blue nevi, and endocrine tumors most commonly manifesting as Cushing’s disease.
Cardiac myxomas may present with obstructive, constitutional, or embolic symptoms.
With left atrial myxoma, symptoms are related to mitral valve obstruction: dizziness, syncope, dyspnea, palpitations, and symptoms of congestive heart failure.
Constitutional symptoms such as fever and weight loss is seen in about 1/3 of patients.
There is significant correlation with serum IL-6 levels and intensity of constitutional symptoms.
Embolic phenomenon is seen in about 29% of patients, and stroke is the most common clinical findings in this regard.
Other embolic phenomenon including myocardial infarction, cutaneous splinter hemorrhages, acro petechiae, and tender erythema may occur.
Cutaneous manifestations may be the first sign of a cardiac myxoma.
Cardiac auscultation may be helpful with a murmur or tumor plop noted and 64% of patients.
EKG may show left atrial hypertrophy.
Diagnosis made with cardiac imaging by electrocardiography.
Treatment of choice is excision of the myxoma.
Recurrent rates after excision range from 0-5%.
