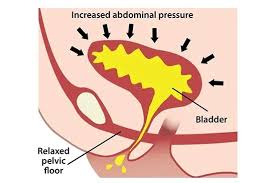
 Mixed incontinence is a condition where a person experiences symptoms of both stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
Mixed incontinence is a condition where a person experiences symptoms of both stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
Mixed urinary incontinence affects 37% of women older than age 65 years.
Stress incontinence involves urine leakage during activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising.
Urge incontinence is characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary urine loss.
Mixed incontinence is common, especially in women.
Mixed incontinence can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Symptoms of mixed incontinence:
Leakage when coughing, sneezing, or during physical activity-stress incontinence.
Sudden, uncontrollable urges to urinate, sometimes resulting in leakage-urge incontinence.
Urination during sleep or immediately after drinking small amounts of liquid.
Mixed incontinence shares causes with both stress and urge incontinence, including:
Pregnancy and childbirth Pelvic surgery or injury Neurological conditions-multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease Aging and menopause
Treatment Bladder training Pelvic floor muscle exercises Medications Behavioral modifications Physical therapy Surgery in select cases
By age 80, 20% women will undergo surgery for stress or mixed urinary incontinence.
Mixed urinary incontinence affects and estimated 30% of female 60 years of age and older.
In women with symptoms of severe urinary incontinence, the cost of supplies, laundry, dry cleaning can be as much as $4000 annually.
OnabotulinumtoxinA treatment can be administered in the clinic or operating room, and requires no incision, but the insertion of the cystoscope.
Midurethral sling surgery is performed in an operating room and typically requires three small incisions and is performed on an outpatient basis.
Sling surgery is meant to be a permanent intervention while OnabotulinumtoxinA is intended to be repeated as the effects of the bladder wear off overtime.
The above measures are utilized in patients who do not respond to conservative treatments and oral medications, and are not different in their efficaciousness and the results are sub optimal as almost half the patients require other measures within a year.
