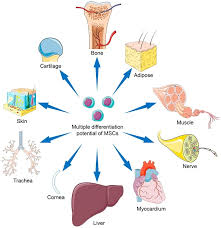
 MSCs are in blood, bone marrow, adipose tissue, skin. trabecular bone, fetal blood, liver and lung tissues.
MSCs are in blood, bone marrow, adipose tissue, skin. trabecular bone, fetal blood, liver and lung tissues.
Composed of less than .01% of bone marrow stromal cells.
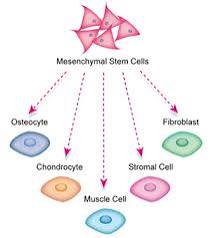
MSCs have limited differentiation capacity.
They are primarily limited to differentiating into cells of mesenchymal origin-fibroblast, osteocytes, adiposite, and chondrocyte.
It is controversial if MSC‘s can be differentiated into cells of endodermal or ectodermal origin.
Bone marrow derived MSCs, represent a nonhematopoietic cell population that can differentiate into mesenchymal tissues-bone cartilage and fat.
MSC’s reside within adipose tissue, bone marrow, Wharton jelly, dental pulp, and may arise from pericytes.
Mesenchymal stem cells from multipotent stromal cells residing in various tissues including the bone marrow, adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle and are able to contribute to tissue repairs and are able differentiating osteoblasts, adipocytes, or chondrocytes.
Plastic adherent MSCs are able to differentiate into a number of mesenchymal cell types including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes and can support hematopoiesis.
MSCs have immunopriveleged and immunosuppressive properties due to the absence of major histocompatibility class II antigens and secretion of T helper type 2 cytokines, respectively.
Estimated that only 30% of clonal MSCs are multipotential (Kuznetsov SA).
Plastic adherent bone marrow MSCs account for 0.01% to 0.0001% of nucleated bone marrow cells.
Can inhibit T cell proliferation, monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells, can suppress natural killer cell cytotoxic effects and modulate B cell functions.
Cell surface markers positive for: Stro-I, CD29, CD73, CD90, CD105, CD166, and CD44.
Cell surface markers negative for: CD31, CD34 ,CD19, CD14, CD1b, CD45, CD79A, and HLA-DR.
These cells are characterized by an absence of hematopoietic stem cell markers.
It is thought that normal MSC function is to migrate to areas of injury and participate in repair processes.
These cells can differentiate into functional cardiomyocytes to improve left ventricular function and remodeling.
Experimental evidence exists that transplantation can help repair myocardium in sheep, have the capacity to generate sarcomeres and electromagnetic coupling and cardiac regeneration.
Injection of mesenchymal precursor cells into the myocardium of patients undergoing a left ventricular assist device implant does not improve the success of weaning of the procedure (Yau MT).
In patients undergoing renal transplant the use of autologous MSCs, compared with anti-IL-2 receptor antibody induction therapy resulted in lower incidence of acute rejection, decreased risk of opportunistic infection, and better renal function at 1 year (Tan J et al).
Mesenchymal stem cells are both immuno privileged and immunosuppressive, having the potential to be used as an allograft.
In a randomized comparison of autografting versus autologous therapy in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy both allogeneic and autologous cells were safe, with both cell types having potential regenerative bioactivity in such patients, particularly by reducing infarct size and improving ventricular remodeling measured by spherocity index (the POSEIDON Randomized Trial).
In the above study the majority of patients receiving allografted cells did not mount increased reactive antibodies in response to therapy.
The findings in the above study suggests that ongoing development of allogeneic MSC therapy in patients with a variety of chronic conditions.
In patients with acute leukemia, prophylactic infusions of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells after haploidentical, hematopoietic stem cell transplant, significantly decreases the incidence and severity of chronic graft versus host disease, as well as acute graft versus host disease, without effect on leukemia relapse, or treatment related adverse events (Huang R).
