 2148
2148
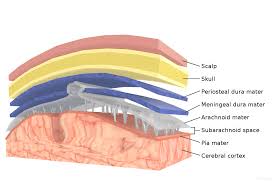
There are three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord.
The meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater.
Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater.
Its primary function is to protect the central nervous system.
The dura mater is a thick, durable membrane, closest to the skull and vertebrae.
The dura mater is the outermost part of the meninges..
The dura mater is a loosely arranged, fibroelastic layer of cells, characterized by multiple interdigitating cell processes, no extracellular collagen, and significant extracellular spaces.
The dura mater center is a mostly fibrous tissue.
The dura mater consists of two layers: the endosteal layer, which lies closest to the skullcap, and the inner meningeal layer, which lies closer to the brain.
The dura mater contains blood vessels that split into the capillaries in the pia mater.
The dura mater’s inner surface is covered by flattened cells like those present on the surfaces of the pia mater and arachnoid mater.
The dura mater envelops the arachnoid mater and surrounds and supports the large dural sinuses carrying blood from the brain toward the heart.
The dura has four areas of infolding:
Falx cerebri- the largest, sickle-shaped; separates the cerebral hemispheres. It attaches to the tentorium cerebellum giving a tentlike appearance.
Tentorium cerebelli, the second largest, crescent-shaped; separates the occipital lobes from cerebellum.
Falx cerebelli lies inferior to the tentorium cerebelli, separating the cerebellar hemispheres.
Diaphragma sellae, smallest infolding; covers the pituitary gland and sella turcica.
Arachnoid mater is the middle element of the meninges.
The arachnoid mater has ac spider web-like appearance, and cushions the central nervous system.
The arachnoid mater has a transparent membrane is composed of fibrous tissue and, is covered by flat cells impermeable to fluid.
The arachnoid does not follow the convolutions of the surface of the brain.
Arachnoid trabeculae filaments pass from the arachnoid through the subarachnoid space to blend the pia mater.
The outermost portion of the arachnoid, the barrier cell layer, is tightly packed with cells representing a barrier between the cerebrospinal fluid and subarachnoid space and the blood circulation in the dura.
The pia mater is a very delicate membrane.
It firmly adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord, following all of the brain’s contours.
It is a very thin membrane composed of fibrous tissue covered on its outer surface by a sheet of flat cells thought to be impermeable to fluid.
The pia mater is pierced by blood vessels to the brain and spinal cord, and its capillaries nourish the brain.
The arachnoid and pia mater together are sometimes called the leptomeninges,
The arachnoid is connected to the pia by cob-web like strands, it is structurally continuous with the pia, hence the name pia-arachnoid or leptomeninges.
The leptomeninges are responsible for the production of beta-trace protein, prostaglandin D synthase, a major cerebrospinal fluid protein .
The subarachnoid space is the space that normally exists between the arachnoid and the pia mater, which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and continues down the spinal cord.
Openings at different points along the subarachnoid space are subarachnoid cisterns which are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The dura mater is attached to the skull.
In the spinal cord, the dura mater is separated from the vertebrae by the epidural space, which contains fat and blood vessels.
The arachnoid is attached to the dura mater.
The pia mater is attached to the central nervous system tissue.
The dura mater and the arachnoid can separate through injury or illness,
The space between the dura mater and the arachnoid is the subdural space.
There is a subpial space underneath the pia mater.
Meningeal injuries can result in a hemorrhage and two types of hematoma.
A subarachnoid hemorrhage is acute bleeding under the arachnoid.
