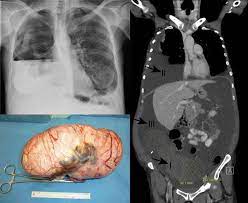
 Meigs’s syndrome is the triad of ascites, pleural effusion, and benign ovarian tumor (ovarian fibroma, fibrothecoma, Brenner tumour, and occasionally granulosa cell tumor).
Meigs’s syndrome is the triad of ascites, pleural effusion, and benign ovarian tumor (ovarian fibroma, fibrothecoma, Brenner tumour, and occasionally granulosa cell tumor).
Meig’s syndrome resolves after the resection of the tumor.
Because the transdiaphragmatic lymphatic channels are larger in diameter on the right, the pleural effusion is classically on the right side.
It is characterized by a benign pelvic mass with right-sided pleural effusion but without ascites, can also occur.
As in typical Meigs syndrome, pleural effusion resolves after removal of the pelvic mass.
Meigs syndrome may mimic other conditions, since it is tumor arising from ovaries, pathology of any organs present in the abdomen may show a similar set of symptoms.
These include various gynecological disorders of the uterus such as endometrial tumor, sarcoma, leiomyoma,fallopian tube disorders such as hydros alpine, granulomatous salpingitis, fallopian tube malignancy; ovarian disorders such as serous, mucinous, endometrioid, or clear cell carcinoma, Brenner tumor, granulosa cell tumor, stromal tumor, dysgerminoma, fibroma, or metastatic tumor to the ovary.
Meigs syndrome is characterized by the presence of a benign solid ovarian tumor associated with ascites and right hydrothorax that disappear after tumor removal.
Non-gynecological manifestations include: ascites, portal vein obstruction, inferior vena cava obstruction, hypoproteinaemia, thoracic duct obstruction, tuberculosis, amyloidosis, exudative pleural effusion, and congestive heart failure.
Clinical condition characterized by ovarian mass, ascites, and right-sided pleural effusion.
Ovarian malignancy and the other causes of pelvic mass, ascites, and pleural effusion are to be considered,
Treatment of Meigs syndrome consists of thoracentesis and paracentesis to drain off the excess fluid, and unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy or wedge resection to correct the underlying cause.
