Rates are increasing up from 30% to 43%.
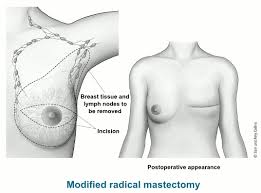
Up to 40% of the 1.7 million women diagnosed with breast cancer each year will require a mastectomy is the surgical treatment for their disease.
Most women undergo breast reconstruction with autologous tissue, an implant or combination of these approaches.
For most breast cancers breastbconserving therapy is the pref2242ed procedure, however in patients with extensive and multicentric disease, mastectomy remains indicated.
Can profoundly affect body image and self-esteem.
Rates are rising for mastectomy among breast cancer patients who are candidates for lumpectomy.
There has also been an increase in the number of patients undergoing contralateral prophylactic mastectomy, despite lack of definitive evidence this this procedure confers surgical advantage.
The use of MRI has increased the rate of mastectomy.
Usually requires a 1-2 day hospitalization.
Results in inability to breast feed, and causes a loss of sensation of the skin of the chest.
Alters personal appearance and can make wearing some clothes difficult.
Associated with anxiety, depression, negative body image and sexual dysfunction.
Prophylactic bilateral mastectomy in high-risk women decreases the risk of breast cancer and associated mortality by 90%.
Higher rates in rural areas.
The incidence of local-regional recurrence after conventional mastectomy ranges from 2.3-10.2%, with variation related to age, stage, therapy, and use of postmastectomy radiation(Fisher B).
Permanently alters the lymphatic drainage pattern to the axilla, so that future sentinel lymph node biopsy is not technically feasible.
MRI studies show that 3% of patients have gross residual breast tissue after mastectomy, 13% after skin sparing mastectomy, and more than 50% of patients after nipple sparing mastectomy.
