Rare sexually related disease by a strain of Chlamydia bacteria-Chlamydia trachoma.
The most common bacterial cause of sexually transmitted genital infection in the US.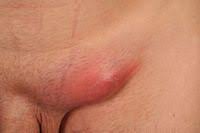
Has two forms: classical , with swelling and inflammation of lymph nodes in the groin sometimes progressing to drainage of pus and occurs in both men and women, and the most common type, today, with proctitis in men having sex with men, associated with pain, bleeding and constipation.
Proctitis form transmitted from rectum to rectum, without penile transmission.
The bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis can cause 2 conditions in humans; trachoma and lymphogranuloma venereum.
Symptoms of lymphogranuloma venereum include pruritus ani, purulent rectal discharge, hematochezia rectal pain and diarrhea or constipation.
Lymphogranuloma venereum can cause fistulas, strictures and anorectal abscesses if left untreated.
It has three stages:
First stage is a small painless, transit ulcer at the site of inoculation.
Second stage 2 to 6 weeks later, large and tender inguinal lymph nodes appear.
The third stage occurs with scarring from chronic lymphadenitis which may appear as lymphedema and genital elephantiasis.
Recommended therapy for LGV is a 21 day regimen of doxycycline
