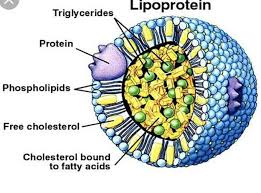
Cholesterol and triglycerides are the major lipids and is transported in plasma by lipoproteins.
Elevated levels of Lipoprotein(a) are associated with major adverse cardiovascular events.
A lipoprotein is composed of cholesterol, triglycerides, and a single apolipoprotein molecule when secreted into plasma by the liver, and is referred to as a very low density lipoprotein (VLDL).
Triglycerides are rapidly removed by the enzyme lipoprotein lipase and used for energy consumption and storage.
When triglycerides are being removed, the lipoprotein is referred to as a VLDL remnant particle.
When most of the triglycerides have been removed, the lipoprotein becomes increasingly dense and is referred to as a low- density lipoprotein (LDL).
A VLDL particle, a remnant particle, and a LDL particle are different names for the same circulating ApoB lipoprotein are different stages in its lifecycle, depending upon the lipid contact that it carries.
Regardless of its lipid content apoB lipoprotein less than 70 nm in diameter can flux across the endothelial barrier, where it may be returned to circulation via the lymphatic system or will become trapped in the artery wall.
The trapping of ApoB lipoprotein in the artery wall and subsequent release of his cholesterol content to macrophages is necessary for the initiation integration of atherosclerotic plaque.
Over time, the atherosclerotic plaque enlarges as more ApoB containing the VLDL remnant, and LDL particles become trapped in the artery wall.
Each apoB- containing lipoprotein has a single apoB molecule.
Plasma apoB concentration is a direct measure of the total number of circulating atherogenic apoB particles that can be trapped in the artery wall.
The standard lipid panel does not typically measure apoB levels, and the number of circulating apoB is indirectly estimated by measuring plasma LDL-C and triglyceride concentration.
LDL-C is an estimate of the total cholesterol content carried by LDL particles, which is an estimate of the concentration of circulating LDL particles.
Plasma triglyceride concentration in milligrams per deciliter divided by five is an estimate of the cholesterol content carried by triglyceride rich Lipo proteins, which is an estimate of the concentration of circulating VLDL and remnant particles.
The above estimates can be combined to derive an estimate of total cholesterol content carried by all apoB particles, referred to as non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol, which in turn is an estimate of the total circulating concentration of all apoB particles.
Guidelines recommending lowering LDL-C with statins, ezetimibe, and proprotein convertase subtilisin/ kexin type 9 inhibitors, because these therapies reduce the risk of arteriosclerotic vascular disease events in randomized trials.
Each of these therapies reduces LDL-C where reducing the number of circulating LDL particles through up regulation of the LDL receptor.
