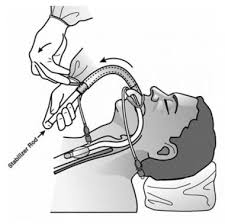
A laryngeal mask airway (LMA) — also known as laryngeal mask — is a medical device that keeps a patient’s airway open during anaesthesia or unconsciousness.
It is a type of supraglottic airway device.
The LMA consists of an airway tube that connects to an elliptical mask with a cuff which is inserted through the patient’s mouth, down the trachea, and once deployed forms an airtight seal on top the glottis.
Tracheal tubes pass through the glottis.
LMA allows a secure airway.
LMAs are most commonly used by anaesthetists to channel oxygen or anaesthesia gas to the lungs during surgery and in the pre-hospital emergency settings for unconscious patients.
The laryngeal mask has an airway tube connecting to an elliptical mask with a cuff.
The cuff can either be an inflating type or self-sealing.
Once inserted the bowl of the mask faces the space between the vocal cords, and the tip of the laryngeal mask sits in the throat against the muscular valve that is located at the upper portion of the esophagus.
The laryngeal mask is widely accepted as a form of airway management.
